Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy potentiates lovastatin-induced apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells
- PMID: 12942316
- PMCID: PMC12161920
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-003-0490-2
Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy potentiates lovastatin-induced apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells
Abstract
Purpose: Mevalonate metabolites are vital for a variety of key cellular functions with the biosynthetic products including cholesterol and farnesyl and geranylgeranyl isoprenoids. Inhibition of this pathway using lovastatin induces a potent apoptotic response in a specific subset of human tumor-derived cell lines, including head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC). In this study, we evaluated the potential of a number of chemotherapeutics that demonstrate activity in HNSCC, including an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) to potentiate the cytotoxic effects of lovastatin.
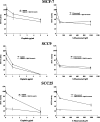
Methods: We evaluated the cytotoxic effects of combining a variety of chemotherapeutics with lovastatin using the MTT assay and flow cytometry. The MCF-7 lovastatin-resistant breast adenocarcinoma cell line and the lovastatin-sensitive HNSCC cell lines SCC9 and SCC25 were tested. Expression levels of EGFR and ligand activated EGFR following lovastatin treatment were analyzed by Western blotting.
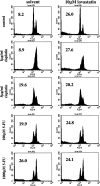
Results: Pretreatment or concomitant treatment of 10 microM lovastatin did not significantly augment the effects of a variety of chemotherapeutic agents tested in these cell lines. Co-administration with actinomycin D or cycloheximide, drugs that inhibit RNA and protein synthesis, respectively, inhibited lovastatin-induced apoptosis in these cell lines. This suggests a requirement for the cellular functions disrupted by these chemotherapeutic agents in lovastatin-induced apoptosis of HNSCC cells. In contrast to the chemotherapeutics analyzed, the AG1478 tyrosine kinase inhibitor of the EGFR demonstrated additive cytotoxic effects in combination with lovastatin in HNSCC cells. Mevalonate metabolites may regulate EGFR function, suggesting that lovastatin may inhibit the activity of this receptor. Indeed, lovastatin treatment inhibited EGF-induced autophosphorylation of the EGFR in the SCC9 and SCC25 cell lines. Pretreatment of SCC9 and SCC25 cell lines for 24 h with 10 microM lovastatin, conditions that demonstrated significant inhibition of EGF-induced EGFR autophosphorylation, induced significant additive effects in combination with AG1478.
Conclusion: These results demonstrated the ability of EGFR pathway inhibitors to potentiate lovastatin-induced apoptosis and suggested that lovastatin may target the EGFR pathway in HNSCC cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Microarray and biochemical analysis of lovastatin-induced apoptosis of squamous cell carcinomas.Neoplasia. 2002 Jul-Aug;4(4):337-46. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900247. Neoplasia. 2002. PMID: 12082550 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine epidermal growth factor receptor ligand production and cetuximab response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 Mar;138(3):491-9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-011-1127-5. Epub 2011 Dec 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22193422 Free PMC article.
-
p16(INK4a) status and survival benefit of EGFR inhibitors in head and neck squamous cell cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018 Apr;124:11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29548481
-
LiGeR-HN phase III trials of petosemtamab + pembrolizumab and petosemtamab monotherapy in recurrent or metastatic HNSCC.Future Oncol. 2025 Jul;21(16):2007-2016. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2511470. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40511820 Free PMC article.
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3:CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3. PMID: 27223332 Updated.
Cited by
-
A phase I study of high-dose rosuvastatin with standard dose erlotinib in patients with advanced solid malignancies.J Transl Med. 2016 Mar 31;14:83. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0836-6. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27036206 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
EGFR-targeted therapy in malignant glioma: novel aspects and mechanisms of drug resistance.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Jan;3(1):37-52. doi: 10.2174/1874467211003010037. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20030624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid raft localization of EGFR alters the response of cancer cells to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Sep;226(9):2316-28. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22570. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21660955 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of statins on dental and oral health: a review of preclinical and clinical studies.J Transl Med. 2020 Apr 6;18(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02326-8. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32252793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simvastatin prevents triple-negative breast cancer metastasis in pre-clinical models through regulation of FOXO3a.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Dec;154(3):495-508. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3645-3. Epub 2015 Nov 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 26590814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal B, Bhendwal S, Halmos B, Moss SF, Ramey WG, Holt PR (1999) Lovastatin augments apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents in colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 5:2223–2229 - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL, Johnson DH (2001) Tyrosine kinase inhibitors-ZD1839 (Iressa). Curr Opin Oncol 13:491–498 - PubMed
-
- Atula T, Silvoniemi P, Kurki T, Varpula M, Grenman R (1997) The evaluation and treatment of the neck in carcinoma of the oral cavity. Acta Otolaryngol [Suppl 5] 29:223–225 - PubMed
-
- Bishayee S (2000) Role of conformational alteration in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) function. Biochem Pharmacol 60:1217–1223 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

