Ssu72 protein mediates both poly(A)-coupled and poly(A)-independent termination of RNA polymerase II transcription
- PMID: 12944462
- PMCID: PMC193702
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.18.6339-6349.2003
Ssu72 protein mediates both poly(A)-coupled and poly(A)-independent termination of RNA polymerase II transcription
Abstract
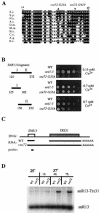
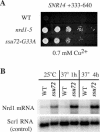
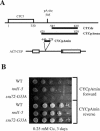
Termination of transcription by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is a poorly understood yet essential step in eukaryotic gene expression. Termination of pre-mRNA synthesis is coupled to recognition of RNA signals that direct cleavage and polyadenylation of the nascent transcript. Termination of nonpolyadenylated transcripts made by Pol II in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, including the small nuclear and small nucleolar RNAs, requires distinct RNA elements recognized by the Nrd1 protein and other factors. We have used genetic selection to characterize the terminator of the SNR13 snoRNA gene, revealing a bipartite structure consisting of an upstream element closely matching a Nrd1-binding sequence and a downstream element similar to a cleavage/polyadenylation signal. Genome-wide selection for factors influencing recogniton of the SNR13 terminator yielded mutations in the gene coding for the essential Pol II-binding protein Ssu72. Ssu72 has recently been found to associate with the pre-mRNA cleavage/polyadenylation machinery, and we find that an ssu72 mutation that disrupts Nrd1-dependent termination also results in deficient poly(A)-dependent termination. These findings extend the parallels between the two termination pathways and suggest that they share a common mechanism to signal Pol II termination.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of cis elements directing termination of yeast nonpolyadenylated snoRNA transcripts.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jul;24(14):6241-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.14.6241-6252.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15226427 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-wide binding sites for components of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae non-poly(A) termination pathway: Nrd1, Nab3, and Sen1.PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002329. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22028667 Free PMC article.
-
cis- and trans-Acting determinants of transcription termination by yeast RNA polymerase II.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(7):2688-96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.7.2688-2696.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16537912 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse and conserved roles of the protein Ssu72 in eukaryotes: from yeast to higher organisms.Curr Genet. 2021 Apr;67(2):195-206. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01132-5. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33244642 Review.
-
The Nrd1-Nab3-Sen1 transcription termination complex from a structural perspective.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Jun 28;51(3):1257-1269. doi: 10.1042/BST20221418. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37222282 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ssu72 phosphatase-dependent erasure of phospho-Ser7 marks on the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain is essential for viability and transcription termination.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):8541-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.335687. Epub 2012 Jan 10. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22235117 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of Transcription by a Splicing-Competent Intron Is Dependent on Promoter Directionality.PLoS Genet. 2016 May 6;12(5):e1006047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006047. eCollection 2016 May. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27152651 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of an intergenic terminator and start site switch that regulate IMD2 transcription in yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;28(12):3883-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00380-08. Epub 2008 Apr 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18426909 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomes of six mutants in the Sen1 pathway reveal combinatorial control of transcription termination across the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome.PLoS Genet. 2017 Jun 30;13(6):e1006863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006863. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28665995 Free PMC article.
-
Nab2 functions in the metabolism of RNA driven by polymerases II and III.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Aug 1;22(15):2729-40. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-01-0055. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21680710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrulis, E. D., J. Werner, A. Nazarian, H. Erdjument-Bromage, P. Tempst, and J. T. Lis. 2002. The RNA processing exosome is linked to elongating RNA polymerase II in Drosophila. Nature 420:837-841. - PubMed
-
- Aranda, A., and N. Proudfoot. 2001. Transcriptional termination factors for RNA polymerase II in yeast. Mol. Cell 7:1003-1011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
