Werner syndrome protein phosphorylation by abl tyrosine kinase regulates its activity and distribution
- PMID: 12944467
- PMCID: PMC193690
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.18.6385-6395.2003
Werner syndrome protein phosphorylation by abl tyrosine kinase regulates its activity and distribution
Abstract
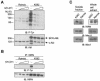
The Werner syndrome protein (WRN) is a caretaker of the human genome, and the Abl kinase is a regulator of the DNA damage response. Aberrant DNA repair has been linked to the development of cancer. Here, we have identified a direct binding between WRN and c-Abl in vitro via the N-terminal and central regions of WRN and the Src homology domain 3 of c-Abl. After bleomycin treatment in culture, WRN and c-Abl are dissociated and followed by an Abl kinase-dependent WRN relocalization to the nucleoplasm. WRN is a substrate of c-Abl in vitro and in vivo. WRN is tyrosine phosphorylated either transiently by treatment of HeLa cells with bleomycin or constitutively in cells from chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients, and these phosphorylations are prevented by treatment with the Abl kinase inhibitor STI-571. Tyrosine phosphorylation of WRN results in inhibition of both WRN exonuclease and helicase activities. Furthermore, anti-WRN immunoprecipitates from CML cells treated with STI-571 show increased 3'-->5' exonuclease activity. These findings suggest a novel signaling pathway by which c-Abl mediates WRN nuclear localization and catalytic activities in response to DNA damage.
Figures




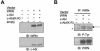

Similar articles
-
Werner protein is a target of DNA-dependent protein kinase in vivo and in vitro, and its catalytic activities are regulated by phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 24;277(21):18291-302. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111523200. Epub 2002 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11889123
-
BCR/ABL stimulates WRN to promote survival and genomic instability.Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 1;71(3):842-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1066. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21123451 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of GSK3β promotes imatinib-mediated apoptosis in quiescent CD34+ chronic myeloid leukemia progenitors, preserving normal stem cells.Blood. 2012 Mar 8;119(10):2335-45. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-06-361261. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22262776
-
Mutated tyrosine kinases as therapeutic targets in myeloid leukemias.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;532:121-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0081-0_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003. PMID: 12908554 Review.
-
Werner syndrome protein: biochemical properties and functional interactions.Exp Gerontol. 2000 Sep;35(6-7):695-702. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(00)00145-5. Exp Gerontol. 2000. PMID: 11053659 Review.
Cited by
-
Collaboration of Werner syndrome protein and BRCA1 in cellular responses to DNA interstrand cross-links.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 May 19;34(9):2751-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl362. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16714450 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium compounds activate ATM-dependent DNA damage response via the mismatch repair protein hMLH1 in colorectal cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 22;285(43):33010-33017. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.137406. Epub 2010 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20709753 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation regulates WRN catalytic activities and affects base excision DNA repair.PLoS One. 2008 Apr 9;3(4):e1918. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001918. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18398454 Free PMC article.
-
A unified view of base excision repair: lesion-dependent protein complexes regulated by post-translational modification.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Jun 1;6(6):695-711. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.01.009. Epub 2007 Mar 6. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17337257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
c-Abl downregulates the slow phase of double-strand break repair.Cell Death Dis. 2010;1(1):e20. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2009.21. Cell Death Dis. 2010. PMID: 21364621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agami, R., G. Blandino, M. Oren, and Y. Shaul. 1999. Interaction of c-Abl and p73α and their collaboration to induce apoptosis. Nature 399:809-813. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, J. S., C. E. Lyon, A. H. Fox, A. K. Leung, Y. W. Lam, H. Steen, M. Mann, and A. I. Lamond. 2002. Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr. Biol. 12:1-11. - PubMed
-
- Baskaran, R., L. D. Wood, L. L. Whitaker, C. E. Canman, S. E. Morgan, Y. Xu, C. Barlow, D. Baltimore, A. Wynshaw-Boris, M. B. Kastan, and J. Y. Wang. 1997. Ataxia telangiectasia mutant protein activates c-Abl tyrosine kinase in response to ionizing radiation. Nature 387:516-519. - PubMed
-
- Blander, G., N. Zalle, Y. Daniely, J. Taplick, M. D. Gray, and M. Oren. 2002. DNA damage-induced translocation of the Werner helicase is regulated by acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:50934-50940. - PubMed
-
- Brosh, R. M., Jr., and V. A. Bohr. 2002. Roles of the Werner syndrome protein in pathways required for maintenance of genome stability. Exp. Gerontol. 37:491-506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
