Nuclear factor of activated T cells c is a target of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in T cells
- PMID: 12944472
- PMCID: PMC193716
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.18.6442-6454.2003
Nuclear factor of activated T cells c is a target of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in T cells
Abstract
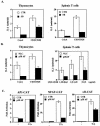
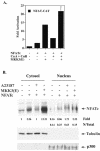
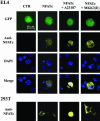
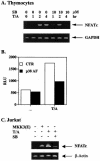
p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) is essential for T-cell activation. Here we demonstrated that nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) is a direct target of p38 MAPK. Inhibition of p38 MAPK led to selective inactivation of NFAT in T cells. We further linked a strict requirement of p38 MAPK to activation of NFATc. A stimulatory effect of p38 MAPK on at least four other stages of NFATc activation was found. First, the p38 MAPK cascade activated the NFATc promoter and induced the transcription of NFATc mRNA. Second, p38 MAPK mildly increased the mRNA stability of NFATc. Third, p38 MAPK enhanced the translation of NFATc mRNA. Fourth, p38 MAPK promoted the interaction of NFATc with the coactivator CREB-binding protein. In contrast, p38 MAPK moderately enhanced the expulsion of NFATc from the nucleus in T cells. Therefore, p38 MAPK has opposite effects on different stages of NFATc activation. All together, the overall effect of p38 MAPK on NFATc in T cells is clear activation.
Figures

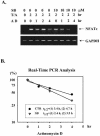


References
-
- Avots, A., M. Buttmann, S. Chuvpilo, C. Escher, U. Smola, A. J. Bannister, U. R. Rapp, T. Kouzarides, and E. Serfling. 1999. CBP/p300 integrates Raf/Rac-signaling pathways in the transcriptional induction of NF-ATc during T cell activation. Immunity 10:515-524. - PubMed
-
- Ballinger, D. G., and M. L. Pardue. 1983. The control of protein synthesis during heat shock in Drosophila cells involved altered polypeptide elongation rate. Cell 33:103-144. - PubMed
-
- Beals, C. R., C. M. Sheridan, C. W. Turck, P. Gardner, and G. R. Crabtree. 1997. Nuclear export of NF-ATc enhanced by glycogen synthase kinase-3. Science 275:1930-1934. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. Y., and A. B. Shyu. 1995. AU-rich elements: characterization and importance in mRNA degradation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 20:465-470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
