Selective degradation of AU-rich mRNAs promoted by the p37 AUF1 protein isoform
- PMID: 12944492
- PMCID: PMC193711
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.18.6685-6693.2003
Selective degradation of AU-rich mRNAs promoted by the p37 AUF1 protein isoform
Abstract
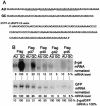
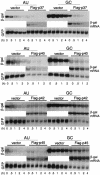
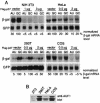
An AU-rich element (ARE) consisting of repeated canonical AUUUA motifs confers rapid degradation to many cytokine mRNAs when present in the 3' untranslated region. Destabilization of mRNAs with AREs (ARE-mRNAs) is consistent with the interaction of ARE-binding proteins such as tristetraprolin and the four AUF1 isoforms. However, the association of the AUF1-mRNA interaction with decreased ARE-mRNA stability is correlative and has not been directly tested. We therefore determined whether overexpression of AUF1 isoforms promotes ARE-mRNA destabilization and whether AUF1 isoforms are limiting components for ARE-mRNA decay. We show that the p37 AUF1 isoform and, to a lesser extent, the p40 isoform possess ARE-mRNA-destabilizing activity when overexpressed. Surprisingly, overexpressed p37 AUF1 also destabilized reporter mRNAs containing a noncanonical but AU-rich 3' untranslated region. Since overexpressed p37 AUF1 could interact in vivo with the AU-rich reporter mRNA, AUF1 may be involved in rapid turnover of mRNAs that lack canonical AREs. Moreover, overexpression of p37 AUF1 restored the ability of cells to rapidly degrade ARE-mRNAs when that ability was saturated and inhibited by overexpression of ARE-mRNAs. Finally, activation of ARE-mRNA decay often involves a translation-dependent step, which was eliminated by overexpression of p37 AUF1. These data indicate that the p37 AUF1 isoform and, to some extent, the p40 isoform are limiting factors that facilitate rapid decay of AU-rich mRNAs.
Figures




Similar articles
-
14-3-3sigma is a p37 AUF1-binding protein that facilitates AUF1 transport and AU-rich mRNA decay.EMBO J. 2006 Aug 23;25(16):3823-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601264. Epub 2006 Aug 10. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16902409 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of functional ribonucleoprotein complexes by AU-rich element RNA-binding protein 1 (AUF1) requires base-dependent and -independent RNA contacts.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 27;288(39):28034-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.489559. Epub 2013 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23940053 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of A+U-rich element binding factor 1 (AUF1)-binding messenger ribonucleic acid correlates with the subcellular relocalization of AUF1 in the rat uterus upon estrogen treatment.Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Sep;18(9):2255-67. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0103. Epub 2004 Jun 10. Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15192077
-
Physiological networks and disease functions of RNA-binding protein AUF1.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 Jul-Aug;5(4):549-64. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1230. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014. PMID: 24687816 Review.
-
The role of AUF1 in regulated mRNA decay.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2010 Nov-Dec;1(3):457-73. doi: 10.1002/wrna.26. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2010. PMID: 21956942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of CD83 expression by AUF1 proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan 7;41(1):206-19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1069. Epub 2012 Nov 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23161671 Free PMC article.
-
AUF1 regulation of coding and noncoding RNA.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017 Mar;8(2):10.1002/wrna.1393. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1393. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017. PMID: 27620010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative 3'UTR analysis allows identification of regulatory clusters that drive Eph/ephrin expression in cancer cell lines.PLoS One. 2008 Jul 23;3(7):e2780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002780. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18648668 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp70 is a novel posttranscriptional regulator of gene expression that binds and stabilizes selected mRNAs containing AU-rich elements.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;33(1):71-84. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01275-12. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23109422 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulatory networks in immunity.Immunol Rev. 2013 May;253(1):253-72. doi: 10.1111/imr.12051. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23550651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blaxall, B. C., L. D. Dwyer-Nield, A. K. Bauer, T. J. Bohlmeyer, A. M. Malkinson, and J. D. Port. 2000. Differential expression and localization of the mRNA binding proteins, AU-rich element mRNA binding protein (AUF1) and Hu antigen R (HuR), in neoplastic lung tissue. Mol. Carcinog. 28:76-83. - PubMed
-
- Blaxall, B. C., A. Pende, S. C. Wu, and J. D. Port. 2002. Correlation between intrinsic mRNA stability and the affinity of AUF1 (hnRNP D) and HuR for A+U-rich mRNAs. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 232:1-11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
