Activity-evoked capacitative Ca2+ entry: implications in synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 12944501
- PMCID: PMC6740588
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-21-07737.2003
Activity-evoked capacitative Ca2+ entry: implications in synaptic plasticity
Abstract
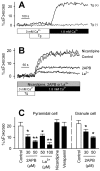
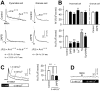
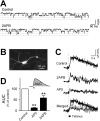
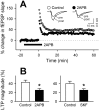
The Ca2+ influx controlled by intracellular Ca2+ stores, called store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOC), occurs in various eukaryotic cells, but whether CNS neurons are endowed with SOC capability and how they may operate have been contentious issues. Using Ca2+ imaging, we present evidence for the presence of SOC in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Depletion of internal Ca2+ stores by thapsigargin caused intracellular Ca2+ elevation, which was prevented by SOC channel inhibitors 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB), SKF96365, and La3+. Interestingly, these inhibitors also accelerated the decay of NMDA-induced Ca2+ transients without affecting their peak amplitude. In addition, SOC channel inhibitors attenuated tetanus-induced dendritic Ca2+ accumulation and long-term potentiation at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses in hippocampal slice preparations. These data suggest a novel link between ionotropic receptor-activated SOC and neuroplasticity.
Figures
References
-
- Baba A, Yamada MK, Nishiyama N, Matsuki N, Ikegaya Y ( 2002) Different Ca2+ dynamics between isolated hippocampal pyramidal cells and dentate granule cells. J Neurocytol 31: 41-48. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ ( 1998) Neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron 21: 13-26. - PubMed
-
- Blaustein MP, Golovina VA ( 2001) Structural complexity and functional diversity of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ stores. Trends Neurosci 24: 602-608. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL ( 1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361: 31-39. - PubMed
-
- Bootman MD, Collins TJ, Mackenzie L, Roderick HL, Berridge MJ, Peppiatt CM ( 2002) 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) is a reliable blocker of store-operated Ca2+ entry but an inconsistent inhibitor of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release. FASEB J 16: 1145-1150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
