Metamorphic T3-response genes have specific co-regulator requirements
- PMID: 12947412
- PMCID: PMC1326352
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor908
Metamorphic T3-response genes have specific co-regulator requirements
Abstract
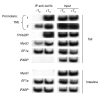
Thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) have several regulatory functions in vertebrates. In the absence of thyroid hormone (T3; tri-iodothyronine), apo-TRs associate with co-repressors to repress transcription, whereas in the presence of T3, holo-TRs engage transcriptional coactivators. Although many studies have addressed the molecular mechanisms of T3 action, it is not known how specific physiological responses arise. We used T3-dependent amphibian metamorphosis to analyse how TRs interact with particular co-regulators to differentially regulate gene expression during development. Using chromatin immuno-precipitation to study tissue from pre-metamorphic tadpoles, we found that TRs are physically associated with T3-responsive promoters, whether or not T3 is present. Addition of T3 results in histone H4 acetylation specifically on T3-response genes. Most importantly, we show that individual T3-response genes have distinct co-regulator requirements, the T3-dependent co-repressor-to-coactivator switch being gene-specific for both co-regulator categories.
Figures



References
-
- Chen H., Lin R.J., Schiltz R.L., Chakravarti D., Nash A., Nagy L., Privalsky M.L., Nakatani Y. & Evans R.M. ( 1999) Nuclear receptor coactivator ACTR is a novel histone acetyltransferase and forms a multimeric activation complex with P/CAF and CBP/p300. Cell, 90, 569–580. - PubMed
-
- Collingwood T.N., Urnov F.D. & Wolffe A.P. ( 1999) Nuclear receptors: coactivators, corepressors and chromatin remodeling in the control of transcription. J. Mol. Endocrinol., 23, 255–275. - PubMed
-
- Fujii G., Tsuchiya R., Itoh Y., Tashiro K. & Hirohashi S. ( 1998) Molecular cloning and expression of Xenopus p300/CBP. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1443, 41–54. - PubMed
-
- Furlow J.D. & Brown D.D. ( 1999) In vitro and in vivo analysis of the regulation of a transcription factor gene by thyroid hormone during Xenopus laevis metamorphosis. Mol. Endocrinol., 13, 2076–2089. - PubMed
-
- Gamble M.J. & Freedman L.P. ( 2002) A coactivator code for transcription. Trends Biochem. Sci., 27, 165–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

