Transforming growth factor beta in cardiovascular development and function
- PMID: 12948523
- PMCID: PMC3855389
- DOI: 10.1016/s1359-6101(03)00044-3
Transforming growth factor beta in cardiovascular development and function
Abstract
Transforming growth factor betas (TGFbetas) are pleiotropic cytokines involved in many biological processes. Genetic engineering and tissue explanation studies have revealed specific non-overlapping roles for TGFbeta ligands and their signaling molecules in development and in normal function of the cardiovascular system in the adult. In the embryo, TGFbetas appear to be involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transformations (EMT) during endocardial cushion formation, and in epicardial epithelial-mesenchymal transformations essential for coronary vasculature, ventricular myocardial development and compaction. In the adult, TGFbetas are involved in cardiac hypertrophy, vascular remodeling and regulation of the renal renin-angiotensin system. The evidence for TGFbeta activities during cardiovascular development and physiologic function will be given and areas which need further investigation will be discussed.
Figures

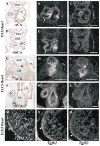
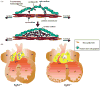

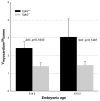
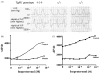
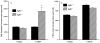
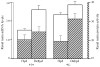
References
-
- Massague J, Chen YG. Controlling TGF-beta signaling. Genes Dev. 2000;14:627–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

