Characterization of dominantly negative mutant ClyA cytotoxin proteins in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 12949101
- PMCID: PMC193753
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.18.5491-5499.2003
Characterization of dominantly negative mutant ClyA cytotoxin proteins in Escherichia coli
Abstract
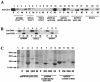
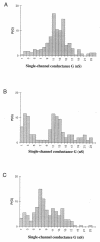
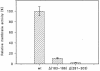
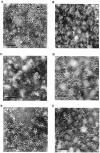
We report studies of the subcellular localization of the ClyA cytotoxic protein and of mutations causing defective translocation to the periplasm in Escherichia coli. The ability of ClyA to translocate to the periplasm was abolished in deletion mutants lacking the last 23 or 11 amino acid residues of the C-terminal region. A naturally occurring ClyA variant lacking four residues (183 to 186) in a hydrophobic subdomain was retained mainly in the cytosolic fraction. These mutant proteins displayed an inhibiting effect on the expression of the hemolytic phenotype of wild-type ClyA. Studies in vitro with purified mutant ClyA proteins revealed that they were defective in formation of pore assemblies and that their activity in hemolysis assays and in single-channel conductance tests was at least 10-fold lower than that of the wild-type ClyA. Tests with combinations of the purified proteins indicated that mutant and wild-type ClyA interacted and that formation of heteromeric assemblies affected the pore-forming activity of the wild-type protein. The observed protein-protein interactions were consistent with, and provided a molecular explanation for, the dominant negative feature of the mutant ClyA variants.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutations affecting export and activity of cytolysin A from Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2010 Aug;192(15):4001-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.01283-09. Epub 2010 May 28. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20511497 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the SlyA-controlled expression, subcellular localization and pore-forming activity of a 34 kDa haemolysin (ClyA) from Escherichia coli K-12.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Jan;31(2):557-67. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01196.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10027972
-
Characterization of variants of the pore-forming toxin ClyA from Escherichia coli controlled by a redox switch.Biochemistry. 2014 Oct 14;53(40):6357-69. doi: 10.1021/bi5007578. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25222267
-
Hemolysin E (HlyE, ClyA, SheA) and related toxins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;677:116-26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6327-7_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20687485 Review.
-
Assembly mechanism of the α-pore-forming toxin cytolysin A from Escherichia coli.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Aug 5;372(1726):20160211. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0211. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28630151 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heat shock proteins IbpA and IbpB are required for NlpI-participated cell division in Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2015 Feb 4;6:51. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00051. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25699035 Free PMC article.
-
On the quantitative treatment of donor-donor energy migration in regularly aggregated proteins.J Fluoresc. 2005 Sep;15(5):797-803. doi: 10.1007/s10895-005-2989-1. J Fluoresc. 2005. PMID: 16341799
-
Delivery of foreign antigens by engineered outer membrane vesicle vaccines.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 16;107(7):3099-104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805532107. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133740 Free PMC article.
-
A highly immunogenic vaccine platform against encapsulated pathogens using chimeric probiotic Escherichia coli membrane vesicles.NPJ Vaccines. 2022 Nov 26;7(1):153. doi: 10.1038/s41541-022-00572-z. NPJ Vaccines. 2022. PMID: 36435869 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of a domain required for protein-protein interactions and inhibitory activity of a Helicobacter pylori dominant-negative VacA mutant protein.Infect Immun. 2006 Apr;74(4):2093-101. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.4.2093-2101.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16552038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrami, L., M. Fivaz, and F. G. van der Goot. 2000. Adventures of a pore-forming toxin at the target cell surface. Trends Microbiol. 8:168-172. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama, Y., S. Kamitani, N. Kusukawa, and K. Ito. 1992. In vitro catalysis of oxidative folding of disulfide-bonded proteins by the Escherichia coli dsbA (ppfA) gene product. J. Biol. Chem. 267:22440-22445. - PubMed
-
- Atkins, A., N. R., Wyborn, A. J. Wallace, T. J. Stillman, L. K. Black, A. B. Fielding, M. Hisakado, P. J. Artymiuk, and J. Green. 2000. Structure-function relationships of a novel bacterial toxin, hemolysin E. The role of alpha G. J. Biol. Chem. 275:41150-41155. - PubMed
-
- Bhakdi, S., H. Bayley, A. Valeva, I. Walev, B. Walker, M. Kehoe, and M. Palmer. 1996. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin, streptolysin-O, and Escherichia coli hemolysin: prototypes of pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Arch. Microbiol. 165:73-79. - PubMed
-
- Braun, V., R. Schonherr, and S. Hobbie. 1993. Enterobacterial hemolysins: activation, secretion and pore formation. Trends Microbiol. 1:211-216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

