Blunted sympathetic vasoconstriction in contracting skeletal muscle of healthy humans: is nitric oxide obligatory?
- PMID: 12949223
- PMCID: PMC2343482
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.049940
Blunted sympathetic vasoconstriction in contracting skeletal muscle of healthy humans: is nitric oxide obligatory?
Abstract
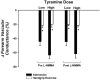
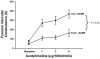
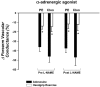
We tested the hypothesis that nitric oxide (NO) is responsible for blunting sympathetic alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction in the active muscles of humans (functional sympatholysis). We measured forearm blood flow (Doppler ultrasound) and calculated the reductions in forearm vascular conductance (FVC) in response to alpha-adrenergic receptor stimulation during rhythmic handgrip exercise and during a control non-exercise vasodilator condition (intra-arterial adenosine), before and after local NO synthase (NOS) inhibition in healthy men. The forearm vasoconstrictor responses to endogenous noradrenaline release (intra-arterial tyramine) were significantly blunted during moderate exercise compared with adenosine, and these vasoconstrictor responses were not restored by NOS inhibition with NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA; n = 6) or NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME; n = 8). Similarly, L-NAME did not restore the vasoconstrictor responses to tyramine in contracting muscle during heavy rhythmic handgrip exercise (n = 4). In four additional subjects, we also found that the vasoconstrictor responses evoked by tyramine during exercise or adenosine were repeatable in the absence of NOS inhibition (i.e. time control). Finally, in five subjects the forearm vasoconstrictor responses to direct alpha 1-adrenergic (phenylephrine) and alpha 2-adrenergic (clonidine) receptor stimulation were blunted during moderate exercise compared with adenosine; these responses were also unaffected by L-NAME. Taken together, our results demonstrate that NO is not obligatory for functional sympatholysis in contracting skeletal muscles of healthy men.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson KM, Faber JE. Differential sensitivity of arteriolar α1- and α2-adrenoceptor constriction to metabolic inhibition during rat skeletal muscle contraction. Circ Res. 1991;69:178–184. - PubMed
-
- Buckwalter JB, Naik JS, Valic Z, Clifford PS. Exercise attenuates alpha-adrenergic-receptor responsiveness in skeletal muscle vasculature. J Appl Physiol. 2001;90:172–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

