GABA mediates autoreceptor feedback inhibition in the rat carotid body via presynaptic GABAB receptors and TASK-1
- PMID: 12949228
- PMCID: PMC2343478
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.048298
GABA mediates autoreceptor feedback inhibition in the rat carotid body via presynaptic GABAB receptors and TASK-1
Abstract
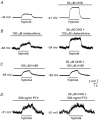
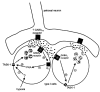
Background K+ channels exert control over neuronal excitability by regulating resting potential and input resistance. Here, we show that GABAB receptor-mediated activation of a background K+ conductance modulates transmission at rat carotid body chemosensory synapses in vitro. Carotid body chemoreceptor (type I) cells expressed GABAB(1) and GABAB(2) subunits as well as endogenous GABA. The GABAB receptor agonist baclofen activated an anandamide- and Ba2+-sensitive TASK-1-like background K+ conductance in chemoreceptor cell clusters, but was without effect on voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Hydroxysaclofen (50 microM), 5-aminovaleric acid (100 microM) and CGP 55845 (100 nM), selective GABAB receptor blockers, potentiated the hypoxia-induced receptor potential; this effect was abolished by pre-treatment with pertussis toxin (PTX; 500 ng ml-1), an inhibitor of Gi, or by H-89 (50 microM), a selective inhibitor of protein kinase A. The protein kinase C inhibitor chelerythrine chloride (100 microM) was without effect on this potentiation. GABAB receptor blockers also caused depolarisation of type I cells in clusters, and enhanced spike discharge in spontaneously firing cells. In functional co-cultures of type I clusters and petrosal sensory neurones, GABAB receptor blockers potentiated hypoxia-induced postsynaptic chemosensory responses mediated by the fast-acting transmitters ACh and ATP. Thus GABAB receptor-mediated activation of TASK-1 or a related channel provides a presynaptic autoregulatory feedback mechanism that modulates fast synaptic transmission in the rat carotid body.
Figures
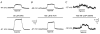
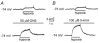

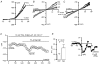

References
-
- Bairam A, Neji H, De Grandpre P, Carroll JL. Autoreceptor mechanism regulating carotid body dopamine release from adult and 10-day-old rabbits. Resp Physiol. 2000;120:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Bayliss DA, Talley EM, Sirois JE, Lei Q. TASK-1 is a highly modulated pH-sensitive ‘leak’ K+ channel expressed in brainstem respiratory neurones. Resp Physiol. 2001;129:159–174. - PubMed
-
- Benot AR, Lopez-Barneo J. Feedback inhibition of Ca2+ currents by dopamine in glomus cells of the carotid body. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2:809–812. - PubMed
-
- Bowery N, Enna SJ. γ-Aminobutyric acidB receptors: first of the functional metabotropic heterodimers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;2:2–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

