Dynamic receptive fields of reconstructed pyramidal cells in layers 3 and 2 of rat somatosensory barrel cortex
- PMID: 12949232
- PMCID: PMC2343497
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.044222
Dynamic receptive fields of reconstructed pyramidal cells in layers 3 and 2 of rat somatosensory barrel cortex
Abstract
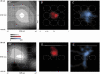
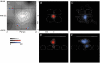
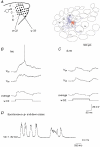
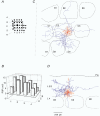
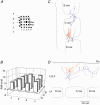
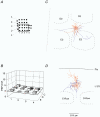
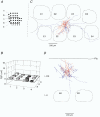
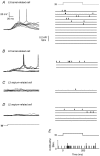
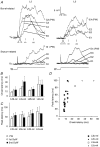
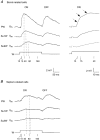
Whole-cell voltage recordings were made in vivo from subsequently reconstructed pyramidal neurons (n = 30) in layer 3 (L3) and layer 2 (L2) of the barrel cortex of urethane-anaesthetised rats. Average resting membrane potentials were well below (15-40 mV) action potential (AP) initiation threshold. The average spontaneous AP activity (0.068 +/- 0.22 APs s-1) was low. Principal whisker (PW) deflections evoked postsynaptic potentials (PSPs) in almost all cells of a PW column but evoked AP activity (0.031 +/- 0.056 APs per PW stimulus 6 deg deflection) was low indicating 'sparse' coding by APs. Barrel-related cells (n = 16) have their soma located above a barrel and project their main axon through the barrel whereas septum-related cells (n = 8) are located above and project their main axon through the septum between barrels. Both classes of cell had broad subthreshold receptive fields (RFs) which comprised a PW and several (> 8) surround whiskers (SuW). Barrel-related cells had shorter PSP onset latencies (9.6 +/- 4.6 ms) and larger amplitude PW stimulus responses (9.1 +/- 4.5 mV) than septum-related cells (23.3 +/- 16.5 ms and 5.0 +/- 2.8 mV, respectively). The dendritic fields of barrel-related cells were restricted, in the horizontal plane, to the PW column width. Their axonal arbors projected horizontally into several SuW columns, preferentially those representing whiskers of the same row, suggesting that they are the major anatomical substrate for the broad subthreshold RFs. In barrel-related cells the response time course varied with whisker position and subthreshold RFs were highly dynamic, expanding in size from narrow single-whisker to broad multi-whisker RFs, elongated along rows within 10-150 ms following a deflection. The response time course in septum-related cells was much longer and almost independent of whisker position. Their broad subthreshold RF suggests that L2/3 cells integrate PSPs from several barrel columns. We conclude that the lemniscal (barrel-related) and paralemniscal (septum-related) afferent inputs remain anatomically and functionally segregated in L2/3.
Figures




References
-
- Ahissar E, Sosnik R, Bagdasarian K, Haidarliu S. Temporal frequency of whisker movement. II. Laminar organization of cortical representations. J Neurophysiol. 2001;86:354–367. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong-James M. The nature and plasticity of sensory processing within adult rat barrel cortex. In: Jones EG, Diamond IT, editors. The Barrel Cortex of Rodents. New York: Plenum Press; 1995. pp. 333–374.
-
- Armstrong-James M, Fox K. Spatio-temporal divergence and convergence in the rat "barrel" cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1987;263:265–281. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong-James M, Fox K, Das-Gupta A. Flow of excitation within rat barrel cortex on striking a single vibrissa. J Neurophysiol. 1992;68:1345–1358. - PubMed
-
- Arnold PB, Li CX, Waters RS. Thalamocortical arbors extend beyond single cortical barrels: an in vivo tracing study in the rat. Exp Brain Res. 2001;136:152–168. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

