Chemical communication among bacteria
- PMID: 12949263
- PMCID: PMC304117
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1934514100
Chemical communication among bacteria
Abstract
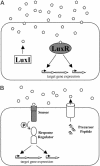
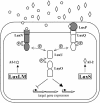
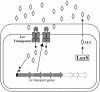
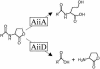
Cell-cell communication in bacteria is accomplished through the exchange of chemical signal molecules called autoinducers. This process, called quorum sensing, allows bacteria to monitor their environment for the presence of other bacteria and to respond to fluctuations in the number and/or species present by altering particular behaviors. Most quorum-sensing systems are species- or group-specific, which presumably prevents confusion in mixed-species environments. However, some quorum-sensing circuits control behaviors that involve interactions among bacterial species. These quorum-sensing circuits can involve both intra- and interspecies communication mechanisms. Finally, anti-quorumsensing strategies are present in both bacteria and eukaryotes, and these are apparently designed to combat bacteria that rely on cell-cell communication for the successful adaptation to particular niches.
Figures

References
-
- Miller, M. B. & Bassler, B. L. (2001) Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55, 165-199. - PubMed
-
- Bassler, B. L. (1999) Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2, 582-587. - PubMed
-
- Fuqua, C., Winans, S. C. & Greenberg, E. P. (1996) Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 50, 727-751. - PubMed
-
- Engebrecht, J., Nealson, K. & Silverman, M. (1983) Cell 32, 773-781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

