The MRN complex: coordinating and mediating the response to broken chromosomes
- PMID: 12949583
- PMCID: PMC1326362
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor925
The MRN complex: coordinating and mediating the response to broken chromosomes
Abstract
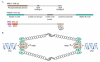
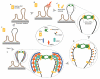
The MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 (MRN) protein complex has been linked to many DNA metabolic events that involve DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs). In vertebrate cells, all three components are encoded by essential genes, and hypomorphic mutations in any of the human genes can result in genome-instability syndromes. MRN is one of the first factors to be localized to the DNA lesion, where it might initially have a structural role by tethering together, and therefore stabilizing, broken chromosomes. This suggests that MRN could function as a lesion-specific sensor. As well as binding to DNA, MRN has other roles in both the processing and assembly of large macromolecular complexes (known as foci) that facilitate efficient DSB responses. Recently, a novel mediator protein, mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1 (MDC1), was shown to co-immunoprecipitate with the MRN complex and regulate MRE11 foci formation. However, whether the initial recruitment of MRN to DSBs requires MDC1 is unclear. Here, we focus on recent developments in MRN research and propose a model for how DSBs are sensed and the cellular responses to them are mediated.
Figures


References
-
- Bakkenist C.J. & Kastan M.B. (2003) DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature, 421, 499–506. - PubMed
-
- Barnes D.E. (2001) Non-homologous end joining as a mechanism of DNA repair. Curr. Biol., 11, R455–R457. - PubMed
-
- Burma S., Chen B.P., Murphy M., Kurimasa A. & Chen D.J. (2001) ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA doublestrand breaks. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 42462–42467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

