Gcn4 occupancy of open reading frame regions results in the recruitment of chromatin-modifying complexes but not the mediator complex
- PMID: 12949586
- PMCID: PMC1326368
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor931
Gcn4 occupancy of open reading frame regions results in the recruitment of chromatin-modifying complexes but not the mediator complex
Abstract
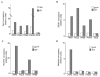
Eukaryotic transcriptional activators usually recognize short DNA motifs, which are not only located within promoter regions, but also scattered throughout the genome. Assuming that the function of activators at non-promoter regions is wasteful and perhaps harmful, one can ask whether such binding is somehow prevented or if transcription is blocked at a downstream step. Here, we show that the yeast transcriptional activator Gcn4 is associated in vivo with several non-promoter euchromatic sites. This association results in the recruitment of the SAGA (Spt3/Ada/Gcn5/acetyltransferase) complex and the consequent activity of the Gcn5 histone acetyltransferase. The functional recruitment of the Swi/Snf nucleosome-remodelling complex was also evident at sites located in positioned nucleosomes. We show that this assemblage of coactivator complexes is not productive because of the absence of core promoter elements, other than the TATA box, that are required for stable mediator recruitment.
Figures

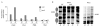

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous recruitment of coactivators by Gcn4p stimulates multiple steps of transcription in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;25(13):5626-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5626-5638.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15964818 Free PMC article.
-
Function and selectivity of bromodomains in anchoring chromatin-modifying complexes to promoter nucleosomes.Cell. 2002 Nov 1;111(3):369-79. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01005-x. Cell. 2002. PMID: 12419247
-
Role for Nhp6, Gcn5, and the Swi/Snf complex in stimulating formation of the TATA-binding protein-TFIIA-DNA complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;24(18):8312-21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.18.8312-8321.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15340090 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of chromatin remodelling factors during gene activation via the glucocorticoid receptor N-terminal domain.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):410-4. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961930 Review.
-
Remodeling chromatin structures for transcription: what happens to the histones?Bioessays. 1996 Nov;18(11):875-84. doi: 10.1002/bies.950181106. Bioessays. 1996. PMID: 8939065 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing the roles of Met31 and Met32 in coordinating Met4-activated transcription in the absence of Met30.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 May;23(10):1928-42. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-06-0532. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22438580 Free PMC article.
-
A role for gcn5-mediated global histone acetylation in transcriptional regulation.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;26(5):1610-6. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.5.1610-1616.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16478983 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the model for coactivator recruitment: Med15 can select its target sites independent of promoter-bound transcription factors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Nov 11;52(20):12093-12111. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae718. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39187372 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription-dependent spreading of the Dal80 yeast GATA factor across the body of highly expressed genes.PLoS Genet. 2019 Feb 28;15(2):e1007999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007999. eCollection 2019 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 30818362 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator influences telomeric silencing and cellular life span.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jun;31(12):2413-21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05242-11. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21482672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown C.E., Howe L., Sousa K., Alley S.C., Carrozza M.J., Tan S. & Workman J.L. ( 2001) Recruitment of HAT complexes by direct activator interactions with the ATM-related Tra1 subunit. Science, 292, 2333–2337. - PubMed
-
- Bryant G.O. & Ptashne M. ( 2003) Independent recruitment in vivo by gal4 of two complexes required for transcription. Mol. Cell, 11, 1301–1309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

