Decreased energetics in murine hearts bearing the R92Q mutation in cardiac troponin T
- PMID: 12952925
- PMCID: PMC182182
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI15967
Decreased energetics in murine hearts bearing the R92Q mutation in cardiac troponin T
Abstract
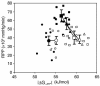
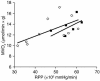
The thin filament protein cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is an important regulator of myofilament activation. Here we report a significant change in cardiac energetics in transgenic mice bearing the missense mutation R92Q within the tropomyosin-binding domain of cTnT, a mutation associated with a clinically severe form of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. This functional domain of cTnT has recently been shown to be a crucial modulator of contractile function despite the fact that it does not directly interact with the ATP hydrolysis site in the myosin head. Simultaneous measurements of cardiac energetics using 31P NMR spectroscopy and contractile performance of the intact beating heart revealed both a decrease in the free energy of ATP hydrolysis available to support contractile work and a marked inability to increase contractile performance upon acute inotropic challenge in hearts from R92Q mice. These results show that alterations in thin filament protein structure and function can lead to significant defects in myocardial energetics and contractile reserve.
Figures
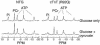
Comment in
-
Cardiac troponin T and familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an energetic affair.J Clin Invest. 2003 Sep;112(5):652-4. doi: 10.1172/JCI19632. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12952912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maron BJ, Bonow RO, Cannon RO, 3rd, Leon MB, Epstein SE. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Interrelations of clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, and therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987;316:780–789. - PubMed
-
- Towbin JA. Molecular genetics of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2000;2:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Tobacman LS, et al. The troponin tail domain promotes a conformational state of the thin filament that suppresses myosin activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:27636–27642. - PubMed
-
- Maytum R, Geeves MA, Lehrer SS. A modulatory role for the troponin T tail domain in thin filament regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:29774–29780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

