Wnt-5a inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway by promoting GSK-3-independent beta-catenin degradation
- PMID: 12952940
- PMCID: PMC2172823
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200303158
Wnt-5a inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway by promoting GSK-3-independent beta-catenin degradation
Abstract
Wnts are secreted signaling molecules that can transduce their signals through several different pathways. Wnt-5a is considered a noncanonical Wnt as it does not signal by stabilizing beta-catenin in many biological systems. We have uncovered a new noncanonical pathway through which Wnt-5a antagonizes the canonical Wnt pathway by promoting the degradation of beta-catenin. This pathway is Siah2 and APC dependent, but GSK-3 and beta-TrCP independent. Furthermore, we provide evidence that Wnt-5a also acts in vivo to promote beta-catenin degradation in regulating mammalian limb development and possibly in suppressing tumor formation.
Figures
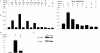
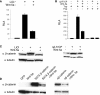
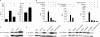
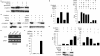


Comment in
-
When Wnts antagonize Wnts.J Cell Biol. 2003 Sep 1;162(5):753-5. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200307181. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12952929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bienz, M., and H. Clevers. 2003. Armadillo/beta-catenin signals in the nucleus—proof beyond a reasonable doubt? Nat. Cell Biol. 5:179–182. - PubMed
-
- Chan, S.K., and G. Struhl. 2002. Evidence that Armadillo transduces wingless by mediating nuclear export or cytosolic activation of Pangolin. Cell. 111:265–280. - PubMed
-
- Chen, R.H., W.V. Ding, and F. McCormick. 2000. Wnt signaling to beta-catenin involves two interactive components. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition and activation of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 275:17894–17899. - PubMed
-
- Crabtree, G.R., and E.N. Olson. 2002. NFAT signaling: choreographing the social lives of cells. Cell. 109(Suppl):S67–S79. - PubMed
-
- DasGupta, R., and E. Fuchs. 1999. Multiple roles for activated LEF/TCF transcription complexes during hair follicle development and differentiation. Development. 126:4557–4568. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

