Thymic medullary epithelial cell differentiation, thymocyte emigration, and the control of autoimmunity require lympho-epithelial cross talk via LTbetaR
- PMID: 12953095
- PMCID: PMC2194183
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030794
Thymic medullary epithelial cell differentiation, thymocyte emigration, and the control of autoimmunity require lympho-epithelial cross talk via LTbetaR
Abstract
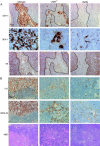
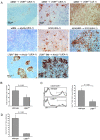
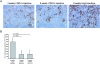
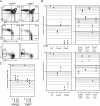
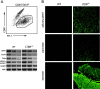
Thymocytes depend on the interaction with thymic epithelial cells for the generation of a diverse, nonautoreactive T cell repertoire. In turn, thymic epithelial cells acquire their three-dimensional cellular organization via instructive signals from developing thymocytes. The nature of these signals has been elusive so far. We show that thymocytes and medullary epithelial cells (MECs) communicate via the lymphotoxin beta receptor (LTbetaR) signaling axis. Normal differentiation of thymic MECs requires LTbetaR ligand on thymocytes and LTbetaR together with nuclear factor-kappaB-inducing kinase (Nik) in thymic epithelial cells. Impaired lympho-epithelial cross talk in the absence of the LTbetaR causes aberrant differentiation and reduced numbers of thymic MECs, leads to the retention of mature T lymphocytes, and is associated with autoimmune phenomena, suggesting an unexpected role for LTbetaR signaling in central tolerance induction.
Figures
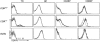

References
-
- van Ewijk, W., G. Hollander, C. Terhorst, and B. Wang. 2000. Stepwise development of thymic microenvironments in vivo is regulated by thymocyte subsets. Development. 127:1583–1591. - PubMed
-
- Laufer, T.M., L.H. Glimcher, and D. Lo. 1999. Using thymus anatomy to dissect T cell repertoire selection. Semin. Immunol. 11:65–70. - PubMed
-
- Klein, L., M. Klugmann, K.A. Nave, V.K. Tuohy, and B. Kyewski. 2000. Shaping of the autoreactive T-cell repertoire by a splice variant of self protein expressed in thymic epithelial cells. Nat. Med. 6:56–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

