Impaired T cell death and lupus-like autoimmunity in T cell-specific adapter protein-deficient mice
- PMID: 12953096
- PMCID: PMC2194195
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021358
Impaired T cell death and lupus-like autoimmunity in T cell-specific adapter protein-deficient mice
Abstract
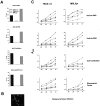
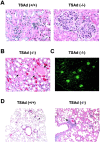
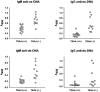
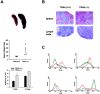
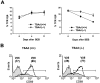
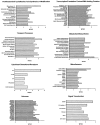
T cell-specific adaptor protein (TSAd) is a T lineage-restricted signaling adaptor molecule that is thought to participate in the assembly of intracellular signaling complexes in T cells. Previous studies of TSAd-deficient mice have revealed a role for TSAd in the induction of T cell interleukin 2 secretion and proliferation. We now show that TSAd-deficient mice are susceptible to lupus-like autoimmune disease. On the nonautoimmune-prone C57BL/6 genetic background, TSAd deficiency results in hypergammaglobulinemia that affects all immunoglobulin (Ig)G subclasses. Older C57BL/6 TSAd-deficient mice (1 yr of age) accumulate large numbers of activated T and B cells in spleen, produce autoantibodies against a variety of self-targets including single stranded (ss) and double stranded (ds) DNA, and, in addition, develop glomerulonephritis. We further show that immunization of younger C57BL/6 TSAd-deficient mice (at age 2 mo) with pristane, a recognized nonspecific inflammatory trigger of lupus, results in more severe glomerulonephritis compared with C57BL/6 controls and the production of high titer ss and ds DNA antibodies of the IgG subclass that are not normally produced by C57BL/6 mice in this model. The development of autoimmunity in TSAd-deficient mice is associated with defective T cell death in vivo. These findings illustrate the role of TSAd as a critical regulator of T cell death whose absence promotes systemic autoimmunity.
Figures
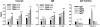
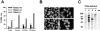

References
-
- Spurkland, A., J.E. Brinchmann, G. Markussen, F. Pedeutour, E. Munthe, T. Lea, F. Vartdal, and H.C. Aasheim. 1998. Molecular cloning of a T cell-specific adapter protein (TSAd) containing an Src homology (SH) 2 domain and putative SH3 and phosphotyrosine binding sites. J. Biol. Chem. 273:4539–4546. - PubMed
-
- Choi, Y.B., C.K. Kim, and Y. Yun. 1999. Lad, an adapter protein interacting with the SH2 domain of p56lck, is required for T cell activation. J. Immunol. 163:5242–5249. - PubMed
-
- Sun, W., K. Kesavan, B.C. Schaefer, T.P. Garrington, M. Ware, N.L. Johnson, E.W. Gelfand, and G.L. Johnson. 2001. MEKK2 associates with the adapter protein Lad/RIBP and regulates the MEK5-BMK1/ERK5 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276:5093–5100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

