Rad52 and Ku bind to different DNA structures produced early in double-strand break repair
- PMID: 12954758
- PMCID: PMC203314
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg729
Rad52 and Ku bind to different DNA structures produced early in double-strand break repair
Abstract
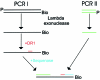
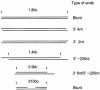
DNA double-strand breaks are repaired by one of two main pathways, non-homologous end joining or homologous recombination. A competition for binding to DNA ends by Ku and Rad52, proteins required for non-homologous end joining and homologous recombination, respectively, has been proposed to determine the choice of repair pathway. In order to test this idea directly, we compared Ku and human Rad52 binding to different DNA substrates. How ever, we found no evidence that these proteins would compete for binding to the same broken DNA ends. Ku bound preferentially to DNA with free ends. Under the same conditions, Rad52 did not bind preferentially to DNA ends. Using a series of defined substrates we showed that it is single-stranded DNA and not DNA ends that were preferentially bound by Rad52. In addition, Rad52 aggregated DNA, bringing different single-stranded DNAs in close proximity. This activity was independent of the presence of DNA ends and of the ability of the single-stranded sequences to form extensive base pairs. Based on these DNA binding characteristics it is unlikely that Rad52 and Ku compete as 'gatekeepers' of different DNA double-strand break repair pathways. Rather, they interact with different DNA substrates produced early in DNA double-strand break repair.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Binding of double-strand breaks in DNA by human Rad52 protein.Nature. 1999 Apr 22;398(6729):728-31. doi: 10.1038/19560. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10227297
-
Biochemical evidence for Ku-independent backup pathways of NHEJ.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Sep 15;31(18):5377-88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg728. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12954774 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Ku heterodimer bound to DNA and its implications for double-strand break repair.Nature. 2001 Aug 9;412(6847):607-14. doi: 10.1038/35088000. Nature. 2001. PMID: 11493912
-
One ring to bring them all--the role of Ku in mammalian non-homologous end joining.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 May;17:30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.02.019. Epub 2014 Mar 26. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24680220 Review.
-
The Ku heterodimer: function in DNA repair and beyond.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015 Jan-Mar;763:15-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jul 4. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 25795113 Review.
Cited by
-
Hierarchy of nonhomologous end-joining, single-strand annealing and gene conversion at site-directed DNA double-strand breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jul;36(12):4088-98. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn347. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18539610 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of nuclear maturation, DNA damage and repair gene expression of bovine oocyte and cumulus cells submitted to ionizing radiation.Anim Reprod. 2023 May 29;20(2):e20230021. doi: 10.1590/1984-3143-AR2023-0021. eCollection 2023. Anim Reprod. 2023. PMID: 37293252 Free PMC article.
-
Rad52 competes with Ku70/Ku86 for binding to S-region DSB ends to modulate antibody class-switch DNA recombination.Nat Commun. 2017 Feb 8;8:14244. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14244. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28176781 Free PMC article.
-
RAD52 is required for RNA-templated recombination repair in post-mitotic neurons.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 26;293(4):1353-1362. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.808402. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29217771 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative-NHEJ is a mechanistically distinct pathway of mammalian chromosome break repair.PLoS Genet. 2008 Jun 27;4(6):e1000110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000110. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18584027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kanaar R., Hoeijmakers,J.H. and van Gent,D.C. (1998) Molecular mechanisms of DNA double strand break repair. Trends Cell Biol., 8, 483–489. - PubMed
-
- Critchlow S.E. and Jackson,S.P. (1998) DNA end-joining: from yeast to man. Trends Biochem. Sci., 23, 394–398. - PubMed
-
- D'Amours D. and Jackson,S.P. (2002) The Mre11 complex: at the crossroads of DNA repair and checkpoint signalling. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 3, 317–327. - PubMed
-
- de Vries E., van Driel,W., Bergsma,W.G., Arnberg,A.C. and van der Vliet,P.C. (1989) HeLa nuclear protein recognizing DNA termini and translocating on DNA forming a regular DNA–multimeric protein complex. J. Mol. Biol., 208, 65–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

