The biological clock nucleus: a multiphasic oscillator network regulated by light
- PMID: 12954869
- PMCID: PMC6740506
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-22-08070.2003
The biological clock nucleus: a multiphasic oscillator network regulated by light
Abstract
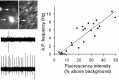
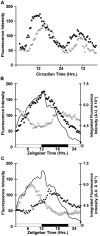
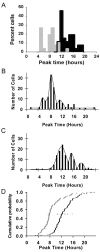
The circadian clock nucleus of the mammalian brain is composed of thousands of oscillator neurons, each driven by the cell-autonomous action of a defined set of circadian clock genes. A critical question is how these individual oscillators are organized into an internal clock that times behavior and physiology. We examined the neural organization of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) through time-lapse imaging of a short-half-life green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter of the circadian clock gene Period 1 (Per1). Using brain slice preparations, Per1 promoter rhythms were resolved at the level of the SCN, and in individual neurons within the SCN, to determine the temporal patterns of rhythmicity resulting from exposure of mice to light/dark cycle (LD) and constant darkness (DD) conditions. Quantitative imaging and patch-clamp electrophysiology were used to define the relationship of Per1 gene expression to neurophysiological output on an individual neuron basis. We found that in both LD and DD, the overall rhythm of the clock nucleus is composed of individual cellular rhythms that peak in distinct phase groups at 3-4 hr intervals. However, the phase relationships of Per1 oscillations to locomotor activity and the phase relationships among individual neuronal oscillators within the SCN are different in LD and DD. There was a positive, linear correlation of Per1 transcription with neuronal spike frequency output, thus Per1::GFP rhythms are representative of physiological rhythmicity. Our results reveal multiple phase groupings of SCN oscillators and suggest that light regulation of oscillator interactions within the SCN underlies entrainment to the photoperiod.
Figures


References
-
- Albrecht U ( 2002) Functional genomics of sleep and circadian rhythm: invited review. Regulation of mammalian circadian clock genes. J Appl Physiol 92: 1348-1355. - PubMed
-
- Bae K, Jin X, Maywood ES, Hastings MH, Reppert SM, Weaver DR ( 2001)Differential functions of mPer1, mPer2, and mPer3 in the SCN circadian clock. Neuron 30: 525-536. - PubMed
-
- Davis FC, Gorski RA ( 1985) Development of hamster circadian rhythms. I. Within-litter synchrony of mother and pup activity rhythms at weaning. Biol Reprod 33: 353-362. - PubMed
-
- Herzog ED, Geusz ME, Khalsa SB, Straume M, Block GD ( 1997) Circadian rhythms in mouse suprachiasmatic nucleus explants on multimicroelectrode plates. Brain Res 757: 285-290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
