MinK-related peptide 2 modulates Kv2.1 and Kv3.1 potassium channels in mammalian brain
- PMID: 12954870
- PMCID: PMC6740484
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-22-08077.2003
MinK-related peptide 2 modulates Kv2.1 and Kv3.1 potassium channels in mammalian brain
Abstract
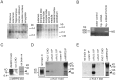
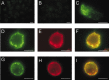
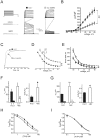
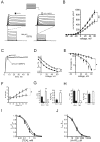
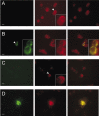
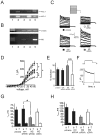
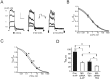
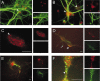
Delayed rectifier potassium current diversity and regulation are essential for signal processing and integration in neuronal circuits. Here, we investigated a neuronal role for MinK-related peptides (MiRPs), membrane-spanning modulatory subunits that generate phenotypic diversity in cardiac potassium channels. Native coimmunoprecipitation from rat brain membranes identified two novel potassium channel complexes, MiRP2-Kv2.1 and MiRP2-Kv3.1b. MiRP2 reduces the current density of both channels, slows Kv3.1b activation, and slows both activation and deactivation of Kv2.1. Altering native MiRP2 expression levels by RNAi gene silencing or cDNA transfection toggles the magnitude and kinetics of endogenous delayed rectifier currents in PC12 cells and hippocampal neurons. Computer simulations predict that the slower gating of Kv3.1b in complexes with MiRP2 will broaden action potentials and lower sustainable firing frequency. Thus, MiRP2, unlike other known neuronal beta subunits, provides a mechanism for influence over multiple delayed rectifier potassium currents in mammalian CNS via modulation of alpha subunits from structurally and kinetically distinct subfamilies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MinK, MiRP1, and MiRP2 diversify Kv3.1 and Kv3.2 potassium channel gating.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 27;279(9):7884-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310501200. Epub 2003 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14679187
-
Delayed rectifier K+ currents, IK, are encoded by Kv2 alpha-subunits and regulate tonic firing in mammalian sympathetic neurons.J Neurosci. 2002 Dec 1;22(23):10094-105. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-23-10094.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12451110 Free PMC article.
-
MiRP2 forms potassium channels in skeletal muscle with Kv3.4 and is associated with periodic paralysis.Cell. 2001 Jan 26;104(2):217-31. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00207-0. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11207363
-
When, where, and how much? Expression of the Kv3.1 potassium channel in high-frequency firing neurons.J Neurobiol. 1998 Oct;37(1):69-79. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4695(199810)37:1<69::aid-neu6>3.0.co;2-6. J Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 9777733 Review.
-
Kv3 channels: voltage-gated K+ channels designed for high-frequency repetitive firing.Trends Neurosci. 2001 Sep;24(9):517-26. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(00)01892-0. Trends Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11506885 Review.
Cited by
-
Modification of K+ channel-drug interactions by ancillary subunits.J Physiol. 2008 Feb 15;586(4):929-50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.139279. Epub 2007 Dec 20. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18096604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Auto-phosphorylation of a voltage-gated K+ channel controls non-associative learning.EMBO J. 2009 Jun 3;28(11):1601-11. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.112. Epub 2009 Apr 23. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19387491 Free PMC article.
-
KCNE1 and KCNE2 inhibit forward trafficking of homomeric N-type voltage-gated potassium channels.Biophys J. 2011 Sep 21;101(6):1354-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.08.015. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21943416 Free PMC article.
-
Homeostatic control of sensory output in basal vomeronasal neurons: activity-dependent expression of ether-à-go-go-related gene potassium channels.J Neurosci. 2009 Jan 7;29(1):206-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3656-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19129398 Free PMC article.
-
The membrane protein MiRP3 regulates Kv4.2 channels in a KChIP-dependent manner.J Physiol. 2010 Jul 15;588(Pt 14):2657-68. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.191395. Epub 2010 May 24. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20498229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott GW, Goldstein SA ( 1998) A superfamily of small potassium channel subunits: form and function of the MinK-related peptides (MiRPs). Q Rev Biophys 31: 357-398. - PubMed
-
- Abbott GW, Goldstein SA ( 2002) Disease-associated mutations in KCNE potassium channel subunits (MiRPs) reveal promiscuous disruption of multiple currents and conservation of mechanism. FASEB J 16: 390-400. - PubMed
-
- Abbott GW, Sesti F, Splawski I, Buck ME, Lehmann MH, Timothy KW, Keating MT, Goldstein SA ( 1999) MiRP1 forms IKr potassium channels with HERG and is associated with cardiac arrhythmia. Cell 97: 175-187. - PubMed
-
- Abbott GW, Goldstein SA, Sesti F ( 2001a) Do all voltage-gated potassium channels use MiRPs? Circ Res 88: 981-983. - PubMed
-
- Abbott GW, Butler MH, Bendahhou S, Dalakas MC, Ptacek LJ, Goldstein SA ( 2001b) MiRP2 forms potassium channels in skeletal muscle with Kv3.4 and is associated with periodic paralysis. Cell 104: 217-231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
