Role of thalamic phospholipase C[beta]4 mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 in inflammatory pain
- PMID: 12954872
- PMCID: PMC6740489
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-22-08098.2003
Role of thalamic phospholipase C[beta]4 mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 in inflammatory pain
Abstract
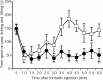
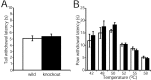
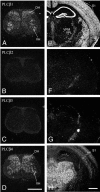
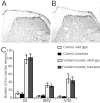
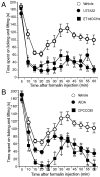
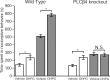
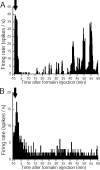
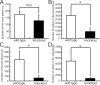
Phospholipase C (PLC) beta4, one of the four isoforms of PLCbetas, is the sole isoform expressed in the mouse ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus (VPL), a key station in pain processing. The mouse thalamus also has been shown to express a high level of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 (mGluR1), which stimulates PLCbetas through activation of Galphaq/11 protein. It is therefore expected that the thalamic mGluR1-PLCbeta4 cascade may play a functional role in nociceptive transmission. To test this hypothesis, we first studied behavioral responses to various nociceptive stimuli in PLCbeta4 knock-out mice. We performed the formalin test and found no difference in the pain behavior in the first phase of the formalin test, which is attributed to acute nociception, between PLCbeta4 knock-out and wild-type mice. Consistent with this result, acute pain responses in the hot plate and tail flick tests were also unaffected in the PLCbeta4 knock-out mice. However, the nociceptive behavior in the second phase of the formalin test, resulting from the tissue inflammation, was attenuated in PLCbeta4 knock-out mice. In the dorsal horn of the spinal cord where PLCbeta1 and PLCbeta4 mRNAs are expressed, no difference was found between the wild-type and knock-out mice in the number of Fos-like immunoreactive neurons, which represent neuronal activity in the second phase in the formalin test. Thus, it is unlikely that spinal PLCbeta4 is involved in the formalin-induced inflammatory pain. Next, we found that pretreatment with PLC inhibitors, mGluR1 antagonists, or both, by either intracerebroventricular or intrathalamic injection, attenuated the formalin-induced pain behavior in the second phase in wild-type mice. Furthermore, activation of mGluR1 at the VPL enhanced pain behavior in the second phase in the wild-type mice. In contrast, PLCbeta4 knock-out mice did not show such enhancement, indicating that mGluR1 is connected to PLCbeta4 in the VPL. Finally, in parallel with the behavioral results, we showed in an electrophysiological study that the time course of firing discharges in VPL corresponds well to that of pain behavior in the formalin test in both wild-type and PLCbeta4 knock-out mice. These findings indicate that the thalamic mGluR1-PLCbeta4 cascade is indispensable for the formalin-induced inflammatory pain by regulating the response of VPL neurons.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tuning thalamic firing modes via simultaneous modulation of T- and L-type Ca2+ channels controls pain sensory gating in the thalamus.J Neurosci. 2008 Dec 3;28(49):13331-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3013-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19052225 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptically driven endocannabinoid release requires Ca2+-assisted metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 1 to phospholipase Cbeta4 signaling cascade in the cerebellum.J Neurosci. 2005 Jul 20;25(29):6826-35. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0945-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16033892 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes 1 and 5 are activators of extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling required for inflammatory pain in mice.J Neurosci. 2001 Jun 1;21(11):3771-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-11-03771.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11356865 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of phospholipase Cbeta4 in synapse elimination and plasticity in developing and mature cerebellum.Mol Neurobiol. 2001 Feb;23(1):69-82. doi: 10.1385/MN:23:1:69. Mol Neurobiol. 2001. PMID: 11642544 Review.
-
The formalin test: an evaluation of the method.Pain. 1992 Oct;51(1):5-17. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90003-T. Pain. 1992. PMID: 1454405 Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption of metabotropic glutamate receptor signalling is a major defect at cerebellar parallel fibre-Purkinje cell synapses in staggerer mutant mice.J Physiol. 2011 Jul 1;589(Pt 13):3191-209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.207563. Epub 2011 May 9. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21558162 Free PMC article.
-
Afferent Fiber Remodeling in the Somatosensory Thalamus of Mice as a Neural Basis of Somatotopic Reorganization in the Brain and Ectopic Mechanical Hypersensitivity after Peripheral Sensory Nerve Injury.eNeuro. 2017 Apr 3;4(2):ENEURO.0345-16.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0345-16.2017. eCollection 2017 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 28396882 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional modulation of fear extinction by mediodorsal thalamic firing in mice.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Dec 25;15(2):308-14. doi: 10.1038/nn.2999. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22197828
-
Tuning thalamic firing modes via simultaneous modulation of T- and L-type Ca2+ channels controls pain sensory gating in the thalamus.J Neurosci. 2008 Dec 3;28(49):13331-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3013-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19052225 Free PMC article.
-
Yin-and-yang bifurcation of opioidergic circuits for descending analgesia at the midbrain of the mouse.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 23;115(43):11078-11083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806082115. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30297409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbadie C, Lombard MC, Morain F, Besson JM ( 1992) Fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat superficial dorsal horn induced by formalin injection in the forepaw: effects of dorsal rhizotomies. Brain Res 578: 17-25. - PubMed
-
- Abbadie C, Taylor BK, Peterson MA, Basbaum AI ( 1997) Differential contribution of the two phases of the formalin test to the pattern of c-fos expression in the rat spinal cord: studies with remifentanil and lidocaine. Pain 69: 101-110. - PubMed
-
- Abe T, Sugihara H, Nawa H, Shigemoto R, Mizuno N, Nakanishi S ( 1992) Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca 2+ signal transduction. J Biol Chem 267: 13361-13368. - PubMed
-
- Berrino L, Oliva P, Rossi F, Palazzo E, Nobili B, Maione S ( 2001) Interaction between metabotropic and NMDA glutamate receptors in the periaqueductal gray pain modulatory system. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 364: 437-443. - PubMed
-
- Bhave G, Karim F, Carlton SM, Gereau RW IV ( 2001) Peripheral group I metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate nociception in mice. Nat Neurosci 4: 417-423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
