Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T-cells)-dependent transcription: a role for the transcription factor NFATc4 in neurotrophin-mediated gene expression
- PMID: 12954875
- PMCID: PMC6740488
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-22-08125.2003
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T-cells)-dependent transcription: a role for the transcription factor NFATc4 in neurotrophin-mediated gene expression
Abstract
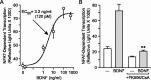
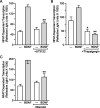
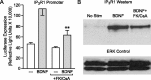
A member of the neurotrophin family, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) regulates neuronal survival and differentiation during development. Within the adult brain, BDNF is also important in neuronal adaptive processes, such as the activity-dependent plasticity that underlies learning and memory. These long-term changes in synaptic strength are mediated through alterations in gene expression. However, many of the mechanisms by which BDNF is linked to transcriptional and translational regulation remain unknown. Recently, the transcription factor NFATc4 (nuclear factor of activated T-cells isoform 4) was discovered in neurons, where it is believed to play an important role in long-term changes in neuronal function. Interestingly, NFATc4 is particularly sensitive to the second messenger systems activated by BDNF. Thus, we hypothesized that NFAT-dependent transcription may be an important mediator of BDNF-induced plasticity. In cultured rat CA3-CA1 hippocampal neurons, BDNF activated NFAT-dependent transcription via TrkB receptors. Inhibition of calcineurin blocked BDNF-induced nuclear translocation of NFATc4, thus preventing transcription. Further, phospholipase C was a critical signaling intermediate between BDNF activation of TrkB and the initiation of NFAT-dependent transcription. Both inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3)-mediated release of calcium from intracellular stores and activation of protein kinase C were required for BDNF-induced NFAT-dependent transcription. Finally, increased expression of IP3 receptor 1 and BDNF after neuronal exposure to BDNF was linked to NFAT-dependent transcription. These results suggest that NFATc4 plays a crucial role in neurotrophin-mediated synaptic plasticity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neurotrophin activation of NFAT-dependent transcription contributes to the regulation of pro-nociceptive genes.J Neurochem. 2007 Aug;102(4):1162-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04632.x. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17488277
-
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells isoform c4 (NFATc4/NFAT3) as a mediator of antiapoptotic transcription in NMDA receptor-stimulated cortical neurons.J Neurosci. 2009 Dec 2;29(48):15331-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4873-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19955386 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:639-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23602987 Review.
-
Neurotrophin-3 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor activate multiple signal transduction events but are not survival factors for hippocampal pyramidal neurons.J Neurochem. 1996 Sep;67(3):952-63. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.67030952.x. J Neurochem. 1996. PMID: 8752100
-
BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: A synthesis and breakdown.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:664-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23831365 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of ryanodine receptors in neurotrophin-induced hippocampal synaptic plasticity and spatial memory formation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 15;108(7):3029-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013580108. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21282625 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking TrkA's trafficking: NGF receptor trafficking controls NGF receptor signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2007 Apr;35(2):151-9. doi: 10.1007/s12035-007-8000-1. Mol Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17917104 Review.
-
Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia Is Associated with Dysregulation of Circadian Rhythm and Adaptive Immune Pathways in the Mouse Trigeminal Ganglia and Nucleus Accumbens.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Dec;56(12):7929-7949. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01650-5. Epub 2019 May 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31129808 Free PMC article.
-
A monoclonal antibody TrkB receptor agonist as a potential therapeutic for Huntington's disease.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 4;9(2):e87923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087923. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24503862 Free PMC article.
-
A network map of BDNF/TRKB and BDNF/p75NTR signaling system.J Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Dec;7(4):301-7. doi: 10.1007/s12079-013-0200-z. Epub 2013 Apr 20. J Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23606317 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ayer-LeLievre C, Olson L, Ebendal T, Seiger A, Persson H ( 1988) Expression of the beta-nerve growth factor gene in hippocampal neurons. Science 240: 1339-1341. - PubMed
-
- Beals CR, Clipstone NA, Ho SN, Crabtree GR ( 1997) Nuclear localization of NF-ATc by a calcineurin-dependent, cyclosporin-sensitive intramolecular interaction. Genes Dev 11: 824-834. - PubMed
-
- Bothwell M ( 1995) Functional interactions of neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 18: 223-253. - PubMed
-
- Carafoli E, Genazzani A, Guerini D ( 1999) Calcium controls the transcription of its own transporters and channels in developing neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 266: 624-632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
