In situ recruitment of antigen-presenting cells by intratumoral GM-CSF gene delivery
- PMID: 12955480
- PMCID: PMC11032855
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-003-0417-4
In situ recruitment of antigen-presenting cells by intratumoral GM-CSF gene delivery
Abstract
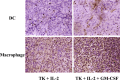
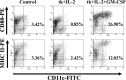
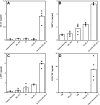
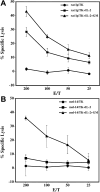
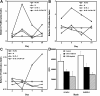
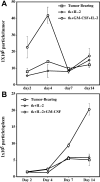
Proper antigen presentation is paramount to the induction of effective and persistent antitumor immune responses. In a murine model of hepatic metastasis of colon cancer, we found that the numbers of in situ mature dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages in tumor-infiltrating leukocytes (TILs) were significantly increased in mice treated with the combination therapy of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase, interleukin 2, and GM-CSF genes when compared with control groups without GM-CSF treatment. Significantly higher levels of IFN-gamma, MIP-1 alpha, mIL-12, and GM-CSF were detected in the tumor after the combination therapy. T cells isolated from the combination therapy-treated mice exhibited higher ex vivo direct CTL activity than those from other treatment groups. Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) enriched from the TILs and liver of the combination therapy-treated mice induced higher levels of proliferation by the splenocytes from long-term surviving mice that had been cured of tumors at early time points (days 4 and 7) whereas significant APC activity was only observed in the spleen at the latter time point (day 7, 14) after the combination therapy. In contrast, APCs isolated from tk or tk + IL-2-treated mice did not induce any significant proliferation. Subcutaneous injection of fluorescence-labeled latex microspheres followed by the combination therapy showed a similar sequential trafficking of microspheres, day 4 after the combination therapy to tumor and day 14 to spleen. The results suggest that APCs recruited by intratumoral gene delivery of GM-CSF can capture antigens, mature to a stage suitable for antigen presentation, and subsequently migrate to the spleen where they can efficiently stimulate antigen-specific T cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase in combination with cytokine gene therapy in an experimental metastatic breast cancer model.Cancer Gene Ther. 2000 Jul;7(7):1086-99. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700215. Cancer Gene Ther. 2000. PMID: 10917212
-
Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor combination gene therapy in a murine CT26 cell colon cancer model.Cancer Gene Ther. 2004 Aug;11(8):570-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700736. Cancer Gene Ther. 2004. PMID: 15232602
-
Dendritic cells infiltrating tumors cotransduced with granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and CD40 ligand genes take up and present endogenous tumor-associated antigens, and prime naive mice for a cytotoxic T lymphocyte response.J Exp Med. 1999 Jul 5;190(1):125-33. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.1.125. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10429676 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor regression induced by intratumor therapy with a disabled infectious single cycle (DISC) herpes simplex virus (HSV) vector, DISC/HSV/murine granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, correlates with antigen-specific adaptive immunity.J Immunol. 2002 Apr 1;168(7):3512-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.7.3512. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11907113
-
The boosting effect of co-transduction with cytokine genes on cancer vaccine therapy using genetically modified dendritic cells expressing tumor-associated antigen.Int J Oncol. 2006 Apr;28(4):947-53. Int J Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16525645
Cited by
-
Development of a successful antitumor therapeutic model combining in vivo dendritic cell vaccination with tumor irradiation and intratumoral GM-CSF delivery.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 Feb;60(2):273-81. doi: 10.1007/s00262-010-0941-y. Epub 2010 Nov 13. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21076828 Free PMC article.
-
Sentinel lymph node as a target of molecular diagnosis of lymphatic micrometastasis and local immunoresponse to malignant cells.Cancer Sci. 2008 Mar;99(3):441-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00672.x. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18070155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenoviral-mediated transfer of human wild-type p53, GM-CSF and B7-1 genes results in growth suppression and autologous anti-tumor cytotoxicity of multiple myeloma cells in vitro.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006 Apr;55(4):375-85. doi: 10.1007/s00262-005-0011-z. Epub 2005 Jul 2. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006. PMID: 16001164 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor effects of combined granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor and macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha plasmid DNA.Cancer Sci. 2010 Nov;101(11):2341-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01704.x. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20804501 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of specific cellular and humoral responses against renal cell carcinoma after combination therapy with cryoablation and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor: a pilot study.J Immunother. 2011 Jun;34(5):457-67. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e31821dcba5. J Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21577139 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

