Exposure of sink drain microcosms to triclosan: population dynamics and antimicrobial susceptibility
- PMID: 12957932
- PMCID: PMC194980
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.9.5433-5442.2003
Exposure of sink drain microcosms to triclosan: population dynamics and antimicrobial susceptibility
Abstract
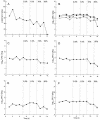
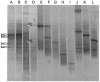
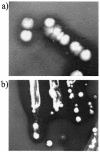
Recent concern that the increased use of triclosan (TCS) in consumer products may contribute to the emergence of antibiotic resistance has led us to examine the effects of TCS dosing on domestic-drain biofilm microcosms. TCS-containing domestic detergent (TCSD) markedly lowered biofouling at 50% (wt/vol) but was poorly effective at use levels. Long-term microcosms were established and stabilized for 6 months before one was subjected to successive 3-month exposures to TCSD at sublethal concentrations (0.2 and 0.4% [wt/vol]). Culturable bacteria were identified by 16S rDNA sequence analysis, and their susceptibilities to four biocides and six antibiotics were determined. Microcosms harbored ca. 10 log(10) CFU/g of biofilm, representing at least 27 species, mainly gamma proteobacteria, and maintained dynamic stability. Viable cell counts were largely unaffected by TCSD exposure, but species diversity was decreased, as corroborated by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis. TCS susceptibilities ranged widely within bacterial groups, and TCS-tolerant strains (including aeromonads, pseudomonads, stenotrophomonads, and Alcaligenes spp.) were isolated before and after TCSD exposure. Several TCS-tolerant bacteria related to Achromobacter xylosoxidans became clonally expanded during dosing. TCSD addition did not significantly affect the community profiles of susceptibility to the test biocides or antibiotics. Several microcosm isolates, as well as reference bacteria, caused clearing of particulate TCS in solid media. Incubations of consortia and isolates with particulate TCS in liquid led to putative TCS degradation by the consortia and TCS solubilization by the reference strains. Our results support the view that low-level exposure of environmental microcosms to TCS does not affect antimicrobial susceptibility and that TCS is degradable by common domestic biofilms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of quaternary-ammonium-based formulations on bacterial community dynamics and antimicrobial susceptibility.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Jun;70(6):3449-56. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.6.3449-3456.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15184143 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation of Biocides Increases Antimicrobial Potency and Mitigates the Enrichment of Nonsusceptible Bacteria in Multispecies Biofilms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Mar 17;83(7):e03054-16. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03054-16. Print 2017 Apr 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28115386 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial characterization of biofilms in domestic drains and the establishment of stable biofilm microcosms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Jan;69(1):177-85. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.1.177-185.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12513993 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilms in vitro and in vivo: do singular mechanisms imply cross-resistance?Symp Ser Soc Appl Microbiol. 2002;(31):98S-110S. Symp Ser Soc Appl Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12481835 Review.
-
Microbial community composition and function in wastewater treatment plants.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002 Aug;81(1-4):665-80. doi: 10.1023/a:1020586312170. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002. PMID: 12448762 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Exposure to Octenidine in a Simulated Sink Trap Environment Results in Selection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Citrobacter, and Enterobacter Isolates with Mutations in Efflux Pump Regulators.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Apr 27;87(10):e00210-21. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00210-21. Print 2021 Apr 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33674437 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Community Establishment, Succession, and Temporal Dynamics in an Industrial Semi-Synthetic Metalworking Fluid Operation: A 50-Week Real-Time Tracking.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 26;12(2):267. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020267. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399671 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmid selection in Escherichia coli using an endogenous essential gene marker.BMC Biotechnol. 2008 Aug 11;8:61. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-8-61. BMC Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18694482 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the immune system by biodiversity from the natural environment: an ecosystem service essential to health.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 12;110(46):18360-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1313731110. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24154724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial activity Study of triclosan-loaded WBPU on Proteus mirabilis in vitro.Int Urol Nephrol. 2017 Apr;49(4):563-571. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1532-z. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28150092
References
-
- Adolfsson-Erici, M., M. Pettersson, J. Parkkonen, and J. Sturve. 2002. Triclosan, a commonly used bactericide found in human milk and in the aquatic environment in Sweden. Chemosphere 46:1485-1489. - PubMed
-
- Allison, D. G., A. J. McBain, and P. Gilbert. 2000. Microbial biofilms: problems of control, p. 310-327. In H. Lappin-Scott, P. Gilbert, M. Wilson, and D. Roberts (ed.), Community structure and cooperation in biofilms. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England.
-
- Ayliffe, G. A., J. R. Babb, J. G. Davies, and H. A Lilly. 1988. Hand disinfection: a comparison of various agents in laboratory and ward studies. J. Hosp. Infect. 11:226-243. - PubMed
-
- Bagley, D. M., and Y. J. Lin. 2000. Clinical evidence for the lack of triclosan accumulation from daily use in dentifrices. Am. J. Dent. 13:148-152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

