Isolation and identification of actinobacteria from surface-sterilized wheat roots
- PMID: 12957950
- PMCID: PMC194995
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.9.5603-5608.2003
Isolation and identification of actinobacteria from surface-sterilized wheat roots
Abstract
This is the first report of filamentous actinobacteria isolated from surface-sterilized root tissues of healthy wheat plants (Triticum aestivum L.). Wheat roots from a range of sites across South Australia were used as the source material for the isolation of the endophytic actinobacteria. Roots were surface-sterilized by using ethanol and sodium hypochlorite prior to the isolation of the actinobacteria. Forty-nine of these isolates were identified by using 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequencing and found to belong to a small group of actinobacterial genera including Streptomyces, Microbispora, Micromonospora, and Nocardiodes spp. Many of the Streptomyces spp. were found to be similar, on the basis of their 16S rDNA gene sequence, to Streptomyces spp. that had been isolated from potato scabs. In particular, several isolates exhibited high 16S rDNA gene sequence homology to Streptomyces caviscabies and S. setonii. None of these isolates, nor the S. caviscabies and S. setonii type strains, were found to carry the nec1 pathogenicity-associated gene or to produce the toxin thaxtomin, indicating that they were nonpathogenic. These isolates were recovered from healthy plants over a range of geographically and temporally isolated sampling events and constitute an important plant-microbe interaction.
Figures
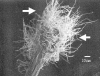
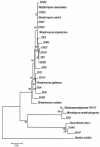

Comment in
-
Isolation and identification of actinobacteria from plant roots.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Jun;70(6):3794; author reply 3794. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.6.3794.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15184195 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Atlas, R. M. 1993. Alphabetical listing of media, p. 455-462. In L. C. Parks (ed.), Handbook of microbiological media. CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, Fla.
-
- Baker, D. D. 1988. Opportunities for autoecological studies of Frankia, a symbiotic actinomycete, p. 271-276. In Y. Okami, T. Beppu, and H. Ogawa (ed.), Biology of actinomycetes. Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on the Biology of Actinomycetes. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, Japan.
-
- Baker, D. D., J. D. Tjepkema, and C. R. Schwintzer. 1990. The biology of Frankia and actinorhizal plants. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, Calif.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

