Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled crossover trial of sustained release morphine for the management of refractory dyspnoea
- PMID: 12958109
- PMCID: PMC192892
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.523
Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled crossover trial of sustained release morphine for the management of refractory dyspnoea
Abstract
Objective: To determine the efficacy of oral morphine in relieving the sensation of breathlessness in patients in whom the underlying aetiology is maximally treated.
Design: Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled crossover study.
Setting: Four outpatient clinics at a hospital in South Australia.
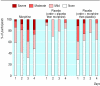
Participants: 48 participants who had not previously been treated with opioids (mean age 76, SD 5) with predominantly chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (42, 88%) were randomised to four days of 20 mg oral morphine with sustained release followed by four days of identically formulated placebo, or vice versa. Laxatives were provided as needed.
Main outcome measures: Dyspnoea in the morning and evening as shown on a 100 mm visual analogue scale, quality of sleep, wellbeing, performance on physical exertion, and side effects as measured at the end of the four day treatment period.
Results: 38 participants completed the study; three withdrew because of definite and two because of possible side effects of morphine (nausea, vomiting, and sedation). Participants reported significantly different dyspnoea scores when treated with morphine: an improvement of 6.6 mm (95% confidence interval 1.6 mm to 11.6 mm) in the morning and of 9.5 mm (3.0 mm to 16.1 mm) in the evening (P = 0.011 and P = 0.006, respectively). During the period in which they were taking morphine participants also reported better sleep (P = 0.039). More participants reported distressing constipation while taking morphine (9 v 1, P = 0.021) in spite of using laxatives. All other side effects were not significantly worse with morphine, although the study was not powered to address side effects.
Conclusions: Sustained release, oral morphine at low dosage provides significant symptomatic improvement in refractory dyspnoea in the community setting.
Figures

Comment in
-
Morphine for management of refractory dyspnoea: opiates should be used with caution.BMJ. 2003 Nov 29;327(7426):1288; author reply 1288-9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7426.1288-b. BMJ. 2003. PMID: 14644985 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Reuben DB, Mor V. Dyspnea in terminally ill cancer patients. Chest 1986;89: 234-6. - PubMed
-
- Burdon JGW, Pain MCF, Rubinfeld AR, Nana A. Chronic lung disease and the perception of breathlessness: a clinical perspective. Eur Respir J 1994;7: 1342-9. - PubMed
-
- O'Driscoll M, Corner J, Bailey C. The experience of breathlessness in lung cancer. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 1999;8: 37-43. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka K, Akechi T, Okuyama T, Nishiwaki Y, Uchitomi Y. Factors correlated with dyspnea in advanced lung cancer patients: organic causes and what else? J Pain Symptom Manage 2002;23: 490-500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
