Chronic, multisite, multielectrode recordings in macaque monkeys
- PMID: 12960378
- PMCID: PMC196923
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1934665100
Chronic, multisite, multielectrode recordings in macaque monkeys
Abstract
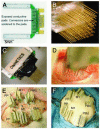
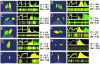
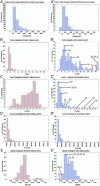
A paradigm is described for recording the activity of single cortical neurons from awake, behaving macaque monkeys. Its unique features include high-density microwire arrays and multichannel instrumentation. Three adult rhesus monkeys received microwire array implants, totaling 96-704 microwires per subject, in up to five cortical areas, sometimes bilaterally. Recordings 3-4 weeks after implantation yielded 421 single neurons with a mean peak-to-peak voltage of 115 +/- 3 microV and a signal-to-noise ratio of better than 5:1. As many as 247 cortical neurons were recorded in one session, and at least 58 neurons were isolated from one subject 18 months after implantation. This method should benefit neurophysiological investigation of learning, perception, and sensorimotor integration in primates and the development of neuroprosthetic devices.
Figures


References
-
- Evarts, E. V. (1960) Fed. Proc. 19, Suppl. 4, 828–837. - PubMed
-
- Wilson, M. A. & McNaughton, B. L. (1993) Science 261, 1055–1058. - PubMed
-
- Nicolelis, M. A. L., Lin, R. C. S., Woodward, D. J. & Chapin, J. K. (1993) Nature 361, 533–536. - PubMed
-
- Nicolelis, M. A. L., Baccala, L. A., Lin, R. C. S. & Chapin, J. K. (1995) Science 268, 1353–1358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

