De novo synthesis of bacterial glycogen: Agrobacterium tumefaciens glycogen synthase is involved in glucan initiation and elongation
- PMID: 12960388
- PMCID: PMC196860
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1534787100
De novo synthesis of bacterial glycogen: Agrobacterium tumefaciens glycogen synthase is involved in glucan initiation and elongation
Abstract
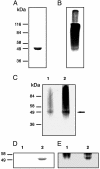
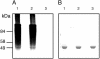
Evidence is presented indicating that initiation of glycogen synthesis in Agrobacterium tumefaciens does not require the presence of alpha(1,4)-linked glucans. Crude cell extracts incubated with ADP-glucose (Glc) were able to form alpha(1,4)-linked glucans despite the fact that cells used for extract preparation displayed a genotype that prevented synthesis of Glc-containing sugar nucleotides and thus preformation of alpha(1,4)-linked glucans and that the defined growth medium used contained glycerol as carbon source. A. tumefaciens glycogen synthase (GS) purified to homogeneity from the above-mentioned cells was able to build its own primer by transferring Glc residues from ADP-Glc to an amino acid(s) in the same protein. Primed GS then became the substrate for further GS-catalyzed glucan elongation. It was concluded that, contrary to what happens in mammalian and yeast cells in which two different proteins are required for linear alpha(1,4)-linked glucan formation (glycogenin for initiation and GS for further elongation), in A. tumefaciens and probably in all other bacteria, the same protein is involved in both glycogen initiation and elongation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
chvA locus may be involved in export of neutral cyclic beta-1,2-linked D-glucan from Agrobacterium tumefaciens.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1989 Jan-Feb;2(1):11-6. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1989. PMID: 2520158
-
Further studies on the primer formation for glycogen biosynthesis in rat heart.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 1993 May;39(3):301-8. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 1993. PMID: 8334383
-
Functional and structural characterization of the catalytic domain of the starch synthase III from Arabidopsis thaliana.Proteins. 2008 Jan 1;70(1):31-40. doi: 10.1002/prot.21469. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 17623838
-
Glycogenin: the primer for mammalian and yeast glycogen synthesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 6;1673(1-2):45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2004.03.017. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15238248 Review.
-
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, a regulatory enzyme for bacterial glycogen synthesis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003 Jun;67(2):213-25, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.2.213-225.2003. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12794190 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coalescence and directed anisotropic growth of starch granule initials in subdomains of Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 26;12(1):6944. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27151-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34836943 Free PMC article.
-
Starch metabolism in Arabidopsis.Arabidopsis Book. 2012;10:e0160. doi: 10.1199/tab.0160. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Arabidopsis Book. 2012. PMID: 23393426 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of the glycogen metabolism pathway underlines a pivotal function of storage polysaccharides in Chlamydiae.Commun Biol. 2021 Mar 5;4(1):296. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01794-y. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33674787 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of glycogen synthase: homologous enzymes catalyze glycogen synthesis and degradation.EMBO J. 2004 Aug 18;23(16):3196-205. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600324. Epub 2004 Jul 22. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15272305 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genome analysis and genome-guided physiological analysis of Roseobacter litoralis.BMC Genomics. 2011 Jun 21;12:324. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-324. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21693016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Preiss, J. & Romeo, T. (1989) Adv. Microb. Physiol. 30, 183–238. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, M. D., Lomako, J., Lomako, W. M. & Whelan, W. J. (1995) FASEB J. 9, 1126–1137. - PubMed
-
- Smythe, C. & Cohen, P. (1991) Eur. J. Biochem. 200, 625–631. - PubMed
-
- Uttaro, A. D. & Ugalde, R. A. (1994) Gene 150, 117–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

