Proteinase-activated receptor 1 activation induces epithelial apoptosis and increases intestinal permeability
- PMID: 12960392
- PMCID: PMC196934
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1831452100
Proteinase-activated receptor 1 activation induces epithelial apoptosis and increases intestinal permeability
Abstract
Proteinase-activated receptor 1 (PAR1)-mediated inflammation remains poorly understood. Here we characterize previously unrecognized effects of PAR1-induced apoptosis signaling, which contributes to epithelial barrier dysfunction. Incubation of epithelial cells with PAR1 agonists induced apoptosis and increased epithelial permeability in a caspase-3-dependent manner. Similarly, studies in vivo demonstrated that intracolonic infusion with PAR1 agonists increased colonic permeability in mice, and that this effect was abolished by pretreatment with a caspase-3 inhibitor. PAR1 agonists induced tight junctional zonula-occludens 1 disruption and apoptotic nuclear condensation. Investigation into signaling pathways showed that these effects were dependent on caspase-3, tyrosine kinase, and myosin light chain kinase. Conversely, the Src kinase inhibitor PP1 augmented zonula-occludens 1 injury and nuclear condensation induced by PAR1 agonists. These results support a role for proteinases and PARs in intestinal disease and provide new directions for possible therapeutic applications of PAR1 antagonists.
Figures
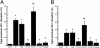
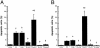
References
-
- Dery, O., Corvera, C. U., Steinhoff, M. & Bunnett, N. W. (1998) Am. J. Physiol. 274, C1429-C1452. - PubMed
-
- Coughlin, S. R. (2000) Nature 407, 258-264. - PubMed
-
- Hollenberg, M. D. & Compton, S. J. (2002) Pharmacol. Rev. 54, 203-217. - PubMed
-
- Buresi, M. C., Schleihauf, E., Vergnolle, N., Buret, A., Wallace, J. L., Hollenberg, M. D. & MacNaughton, W. K. (2001) Am. J. Physiol. 281, G323-G332. - PubMed
-
- Buresi, M. C., Buret, A. G., Hollenberg, M. D. & MacNaughton, W. K. (2002) FASEB J. 16, 1515-1525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

