Rho-dependent formation of epithelial "leader" cells during wound healing
- PMID: 12960404
- PMCID: PMC196881
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1834401100
Rho-dependent formation of epithelial "leader" cells during wound healing
Abstract
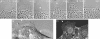
The motile behavior of epithelial cells located at the edge of a large wound in a monolayer of cultured cells was analyzed. The initial cellular response is alignment of the edge with an accompanying formation of tangential marginal actin bundles within individual cells positioned along the wound edge. Later, coherent out-growths of cell masses occur by the formation of special "leader" cells at the tops of outgrowths and "follower" cells along the sides. Leader cells exhibit profound cytoskeletal reorganization, including disassembly of marginal bundles, the realignment of actin filament bundles, and penetration of microtubules into highly active lamellae. Additionally, cell-cell contacts acquire radial geometry indicative of increased contractile tension. Interestingly, leader cells acquire a cytoskeletal organization and motility typical of fibroblasts. IAR-2 cultures stably transfected with a dominant-negative mutant of RhoA or treated with Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 transformed most edge cells into leader-like cells. Alternatively, transfection of cells with constitutively active RhoA suppressed formation of leaders. Thus, expansion of the epithelial sheet involves functional differentiation into two distinct types of edge cells. The transition between these two patterns is controlled by Rho activity, which in turn controls the dynamic distribution and activity of actin filament bundles, myosin II, and microtubules.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RhoA and Rac1 are both required for efficient wound closure of airway epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004 Dec;287(6):L1134-44. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00022.2004. Epub 2004 Aug 6. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15298851
-
Polyamines regulate Rho-kinase and myosin phosphorylation during intestinal epithelial restitution.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003 Apr;284(4):C848-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00371.2002. Epub 2002 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12466151
-
Rearrangements of the actin cytoskeleton and E-cadherin-based adherens junctions caused by neoplasic transformation change cell-cell interactions.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 30;4(11):e8027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008027. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19956566 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin 2 regulates intestinal epithelial cell spreading and wound closure through Rho-related signaling.Am J Pathol. 2007 Mar;170(3):951-66. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060647. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17322380 Free PMC article.
-
Microfilaments in cellular and developmental processes.Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):135-43. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.135. Science. 1971. PMID: 5538822
Cited by
-
Regulation of collective cell migration by RhoGAP myosin IXA.Small GTPases. 2012 Oct-Dec;3(4):213-8. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.20495. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Small GTPases. 2012. PMID: 22735295 Free PMC article.
-
Collective migration of an epithelial monolayer in response to a model wound.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 9;104(41):15988-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705062104. Epub 2007 Sep 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17905871 Free PMC article.
-
Rho family GTPase functions in Drosophila epithelial wound repair.Small GTPases. 2015;6(1):28-35. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.982415. Small GTPases. 2015. PMID: 25862164 Free PMC article.
-
Velocity fields in a collectively migrating epithelium.Biophys J. 2010 May 19;98(9):1790-800. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.01.030. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20441742 Free PMC article.
-
Orientation and polarity in collectively migrating cell structures: statics and dynamics.Biophys J. 2011 Jun 8;100(11):2566-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.04.047. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21641301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trinkaus, J. P. (1984) Cells into Organs: The Forces that Shape the Embryo (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ), 2nd Ed.
-
- Kaltschmidt, J. A., Lawrence, N., Morel, V., Balayo, T., Fernandez, B. G., Plissier, A., Jacinto, A. & Arias, A. M. (2002) Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 937–944. - PubMed
-
- Nodder, S. & Martin, P. (1997) Anat. Embryol. 195, 215–228. - PubMed
-
- Wood, W., Jacinto, A., Grose, R., Woolner, S., Gale, J., Wilson, C. & Martin, P. (2002) Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 907–912. - PubMed
-
- Ridley, A. J. (2001) Trends Cell Biol. 11, 471–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

