Genetic and biochemical evaluation of the importance of Cdc6 in regulating mitotic exit
- PMID: 12960422
- PMCID: PMC313736
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-06-0384
Genetic and biochemical evaluation of the importance of Cdc6 in regulating mitotic exit
Erratum in
- Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1568
Abstract
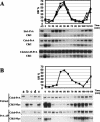
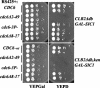
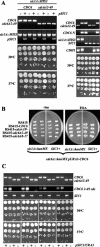
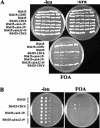
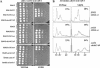
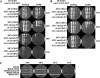
We evaluated the hypothesis that the N-terminal region of the replication control protein Cdc6 acts as an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) activity, promoting mitotic exit. Cdc6 accumulation is restricted to the period from mid-cell cycle until the succeeding G1, due to proteolytic control that requires the Cdc6 N-terminal region. During late mitosis, Cdc6 is present at levels comparable with Sic1 and binds specifically to the mitotic cyclin Clb2. Moderate overexpression of Cdc6 promotes viability of CLB2Deltadb strains, which otherwise arrest at mitotic exit, and rescue is dependent on the N-terminal putative Cdk-inhibitory domain. These observations support the potential for Cdc6 to inhibit Clb2-Cdk, thus promoting mitotic exit. Consistent with this idea, we observed a cytokinesis defect in cdh1Delta sic1Delta cdc6Delta2-49 triple mutants. However, we were able to construct viable strains, in three different backgrounds, containing neither SIC1 nor the Cdc6 Cdk-inhibitory domain, in contradiction to previous work. We conclude, therefore, that although both Cdc6 and Sic1 have the potential to facilitate mitotic exit by inhibiting Clb2-Cdk, mitotic exit nevertheless does not require any identified stoichiometric inhibitor of Cdk activity.
Figures



References
-
- Aitchison, J.D., Blobel, G., and Rout, M.P. (1996). Kap104p: a karyopherin involved in the nuclear transport of messenger RNA binding proteins. Science 274, 624-627. - PubMed
-
- Bardin, A.J., and Amon, A. (2001). Men and sin: what's the difference? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 815-826. - PubMed
-
- Beavis, R.C., and Chait, B.T. (1996). Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass-spectrometry of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 270, 519-551. - PubMed
-
- Bell, S.P., and Dutta, A. (2002). DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 333-374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

