Polarization of specific tropomyosin isoforms in gastrointestinal epithelial cells and their impact on CFTR at the apical surface
- PMID: 12960432
- PMCID: PMC266757
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-03-0169
Polarization of specific tropomyosin isoforms in gastrointestinal epithelial cells and their impact on CFTR at the apical surface
Abstract
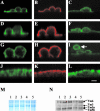
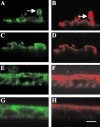
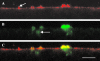
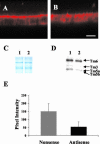
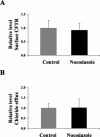
Microfilaments have been reported to be polarized in a number of cell types based both on function and isoform composition. There is evidence that microfilaments are involved in the movement of vesicles and the polarized delivery of proteins to specialized membrane domains. We have investigated the composition of actin microfilaments in gastrointestinal epithelial cells and their role in the delivery of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) into the apical membrane using cultured T84 cells as a model. We identified a specific population of microfilaments containing the tropomyosin (Tm) isoforms Tm5a and/or Tm5b, which are polarized in T84 cell monolayers. Polarization of this microfilament population occurs very rapidly in response to cell-cell and cell-substratum contact and is not inhibited by jasplakinolide, suggesting this involves the movement of intact filaments. Colocalization of Tm5a and/or Tm5b and CFTR was observed in long-term cultures. A reduction in Tm5a and Tm5b expression, induced using antisense oligonucleotides, resulted in an increase in both CFTR surface expression and chloride efflux in response to cAMP stimulation. We conclude that Tm isoforms Tm5a and/or Tm5b mark an apical population of microfilaments that can regulate the insertion and/or retention of CFTR into the plasma membrane.
Figures





References
-
- Ameen, N.A., Ardito, T., Kashgarian, M., and Marino, C.R. (1995). A unique subset of rat and human intestinal villus cells express the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Gastroenterology 108, 1016-1023. - PubMed
-
- Ameem. N.A., Martensson, B., Bourguinon, L., Marino, C., Isenberg, J., McLaughlin, G. E. CFTR. (1999). channel insertion to the apical surface in rat duodenal villus epithelial cells is upregulated by VIP in vivo. J. Cell Sci. 112, 887-894. - PubMed
-
- Chasan, B., Geisse, N.A., Pedatella, K. Wooster, D.G., Teintze, M., Carattino, M.D., Goldmann, W.H., Cantiello, H.F. (2002). Evidence for direct interaction between actin and the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Eur. Biophys. J. 30, 617-624. - PubMed
-
- Drubin, D.G., and Nelson, W.J. (1996). Origins of cell polarity. Cell 84, 335-344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

