Recycling of Raft-associated prohormone sorting receptor carboxypeptidase E requires interaction with ARF6
- PMID: 12960436
- PMCID: PMC266764
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-11-0758
Recycling of Raft-associated prohormone sorting receptor carboxypeptidase E requires interaction with ARF6
Abstract
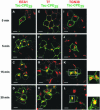
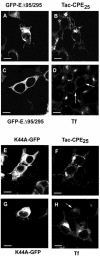
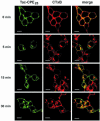
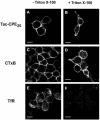
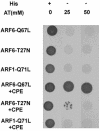
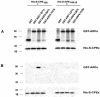
Little is known about the molecular mechanism of recycling of intracellular receptors and lipid raft-associated proteins. Here, we have investigated the recycling pathway and internalization mechanism of a transmembrane, lipid raft-associated intracellular prohormone sorting receptor, carboxypeptidase E (CPE). CPE is found in the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and secretory granules of (neuro)endocrine cells. An extracellular domain of the IL2 receptor alpha-subunit (Tac) fused to the transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic tail of CPE (Tac-CPE25) was used as a marker to track recycling of CPE. We show in (neuro)endocrine cells, that upon stimulated secretory granule exocytosis, raft-associated Tac-CPE25 was rapidly internalized from the plasma membrane in a clathrin-independent manner into early endosomes and then transported through the endocytic recycling compartment to the TGN. A yeast two-hybrid screen and in vitro binding assay identified the CPE cytoplasmic tail sequence S472ETLNF477 as an interactor with active small GTPase ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) 6, but not ARF1. Expression of a dominant negative, inactive ARF6 mutant blocked this recycling. Mutation of residues S472 or E473 to A in the cytoplasmic tail of CPE obliterated its binding to ARF6, and internalization from the plasma membrane of Tac-CPE25 mutated at S472 or E473 was significantly reduced. Thus, CPE recycles back to the TGN by a novel mechanism requiring ARF6 interaction and activity.
Figures



References
-
- Bamezai, A., Goldmacher, V.S., and Rock, K.L. (1992). Internalization of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored lymphocyte proteins. II. GPI-anchored and transmembrane molecules internalize through distinct pathways. Eur. J. Immunol. 22, 15-21. - PubMed
-
- Benmerah, A., Bayrou, M., Cerf-Bensussan, N., and Dautry-Varsat, A. (1999). Inhibition of clathrin-coated pit assembly by an Eps15 mutant. J. Cell Sci. 112, 1303-1311. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

