Rapid microtubule-dependent induction of neurite-like extensions in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts by inhibition of ROCK and Cbl
- PMID: 12960437
- PMCID: PMC266776
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-11-0739
Rapid microtubule-dependent induction of neurite-like extensions in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts by inhibition of ROCK and Cbl
Abstract
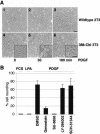
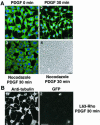
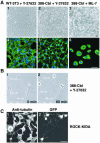
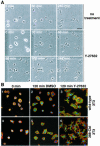
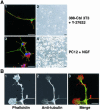
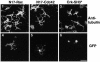
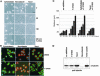
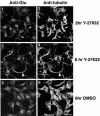
A number of key cellular functions, such as morphological differentiation and cell motility, are closely associated with changes in cytoskeletal dynamics. Many of the principal signaling components involved in actin cytoskeletal dynamics have been identified, and these have been shown to be critically involved in cell motility. In contrast, signaling to microtubules remains relatively uncharacterized, and the importance of signaling pathways in modulation of microtubule dynamics has so far not been established clearly. We report here that the Rho-effector ROCK and the multiadaptor proto-oncoprotein Cbl can profoundly affect the microtubule cytoskeleton. Simultaneous inhibition of these two signaling molecules induces a dramatic rearrangement of the microtubule cytoskeleton into microtubule bundles. The formation of these microtubule bundles, which does not involve signaling by Rac, Cdc42, Crk, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and Abl, is sufficient to induce distinct neurite-like extensions in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts, even in the absence of microfilaments. This novel microtubule-dependent function that promotes neurite-like extensions is not dependent on net changes in microtubule polymerization or stabilization, but rather involves selective elongation and reorganization of microtubules into long bundles.
Figures
References
-
- Aspenstrom, P. (1999). Effectors for the Rho GTPases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11, 95-102. - PubMed
-
- Bachmaier, K., Krawczyk, C., Kozieradzki, I., Kong, Y., Sasaki, T., Olivierados-santos, A., Mariathasan, S.D.B., Wakeham, A., Itle, A., et al. (2000) Negative regulation of lymphocyte activation and autoimmunity by the molecular adaptor Cbl-b. Nature 403, 211-216. - PubMed
-
- Bito, H., Furuyashiki, T., Ishihara, H., Shibasaki, Y., Ohashi, K., Mizuno, K., Maekewa, M., Ishizaki, T., and Narumiya, S. (2000). A critical role for a Rho-associated kinase, p160ROCK in determination of axon outgrowth in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuron 26, 431-441. - PubMed
-
- Chiang, Y.J., Kole, H., Brown, K., Naramura, M., Fukuhara, S., Hu, R.J., Kyung, J., Gutkind, J.S., Shevach, E., and Gu, H. (2000). Cbl-b regulates the CD28 dependence of T-cell activation. Nature 403, 216-220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

