Selective generation of gut tropic T cells in gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT): requirement for GALT dendritic cells and adjuvant
- PMID: 12963696
- PMCID: PMC2194196
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20031244
Selective generation of gut tropic T cells in gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT): requirement for GALT dendritic cells and adjuvant
Abstract
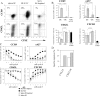
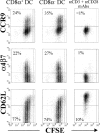
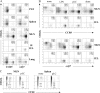
In the current study, we address the underlying mechanism for the selective generation of gut-homing T cells in the gut-associated lymphoid tissues (GALT). We demonstrate that DCs in the GALT are unique in their capacity to establish T cell gut tropism but in vivo only confer this property to T cells in the presence of DC maturational stimuli, including toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent adjuvants. Thus, DCs from mesenteric LNs (MLNs), but not from spleen, supported expression of the chemokine receptor CCR9 and integrin alpha4beta7 by activated CD8+ T cells. While DCs were also required for an efficient down-regulation of CD62L, this function was not restricted to MLN DCs. In an adoptive CD8+ T cell transfer model, antigen-specific T cells entering the small intestinal epithelium were homogeneously CCR9+alpha4beta7+CD62Llow, and this phenotype was only generated in GALT and in the presence of adjuvant. Consistent with the CCR9+ phenotype of the gut-homing T cells, CCR9 was found to play a critical role in the localization of T cells to the small intestinal epithelium. Together, these results demonstrate that GALT DCs and T cell expression of CCR9 play critical and integrated roles during T cell homing to the gut.
Figures

References
-
- Kunkel, E.J., and E.C. Butcher. 2002. Chemokines and the tissue-specific migration of lymphocytes. Immunity. 16:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Berlin, C., R.F. Bargatze, J.J. Campbell, U.H. von Andrian, M.C. Szabo, S.R. Hasslen, R.D. Nelson, E.L. Berg, S.L. Erlandsen, and E.C. Butcher. 1995. alpha 4 integrins mediate lymphocyte attachment and rolling under physiologic flow. Cell. 80:413–422. - PubMed
-
- Zabel, B.A., W.W. Agace, J.J. Campbell, H.M. Heath, D. Parent, A.I. Roberts, E.C. Ebert, N. Kassam, S. Qin, M. Zovko, et al. 1999. Human G protein–coupled receptor GPR-9-6/CC chemokine receptor 9 is selectively expressed on intestinal homing T lymphocytes, mucosal lymphocytes, and thymocytes and is required for thymus-expressed chemokine-mediated chemotaxis. J. Exp. Med. 190:1241–1256. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kunkel, E.J., J.J. Campbell, G. Haraldsen, J. Pan, J. Boisvert, A.I. Roberts, E.C. Ebert, M.A. Vierra, S.B. Goodman, M.C. Genovese, et al. 2000. Lymphocyte CC chemokine receptor 9 and epithelial thymus-expressed chemokine (TECK) expression distinguish the small intestinal immune compartment: epithelial expression of tissue-specific chemokines as an organizing principle in regional immunity. J. Exp. Med. 192:761–768. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wurbel, M.A., J.M. Philippe, C. Nguyen, G. Victorero, T. Freeman, P. Wooding, A. Miazek, M.G. Mattei, M. Malissen, B.R. Jordan, et al. 2000. The chemokine TECK is expressed by thymic and intestinal epithelial cells and attracts double- and single-positive thymocytes expressing the TECK receptor CCR9. Eur. J. Immunol. 30:262–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

