Structural features of the acyl chain determine self-phospholipid antigen recognition by a CD1d-restricted invariant NKT (iNKT) cell
- PMID: 12963715
- PMCID: PMC3465362
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M308089200
Structural features of the acyl chain determine self-phospholipid antigen recognition by a CD1d-restricted invariant NKT (iNKT) cell
Abstract
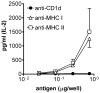
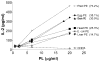
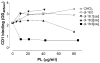
Little is known about the antigen specificity of CD1d-restricted T cells, except that they frequently recognize CD1d-expressing antigen-presenting cells in the absence of exogenous antigen. We previously demonstrated that the 24.8.A iNKT cell hybridoma was broadly reactive with CD1d-transfected cell lines and recognized the polar lipid fraction of a tumor cell extract. In the present study, the antigen recognized by the 24.8.A iNKT cell hybridoma was purified to homogeneity and identified as palmitoyl-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (16:0-18:1 PE). The 24.8.A iNKT cell hybridoma recognized synthetic 16:0-18:1[cis] PE, confirming that this phospholipid is antigenic. Recognition correlated with the degree of unsaturation of the acyl chains. Using a panel of synthetic PEs, the 24.8.A iNKT cell hybridoma was shown to be activated by PEs that contained at least one unsaturated acyl chain. The configuration of the double bonds was important, as the 24.8.A iNKT cell hybridoma recognized unsaturated acyl chains in the cis, but not the trans, configuration. PEs with multiple double bonds were recognized better than those with a single double bond, and increasing acyl chain unsaturation correlated with increased binding of PE to CD1d. These data illustrate the potential importance of the acyl chain structure for phospholipid antigen binding to CD1d.
Figures
References
-
- Miyamoto K, Miyake S, Yamamura T. Nature. 2001;413:531–534. - PubMed
-
- Cui J, Shin T, Kawano T, Sato H, Kondo E, Toura I, Kaneko Y, Koseki H, Kanno M, Taniguchi M. Science. 1997;278:1623–1626. - PubMed
-
- Kawano T, Nakayama T, Kamada N, Kaneko Y, Harada M, Ogura N, Akutsu Y, Motohashi S, Iizasa T, Endo H, Fujisawa T, Shinkai H, Taniguchi M. Cancer Res. 1999;59:5102–5105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

