Contraction-mediated glycogenolysis in mouse skeletal muscle lacking creatine kinase: the role of phosphorylase b activation
- PMID: 12963789
- PMCID: PMC2343558
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.051078
Contraction-mediated glycogenolysis in mouse skeletal muscle lacking creatine kinase: the role of phosphorylase b activation
Abstract
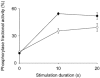
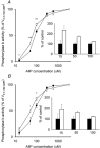
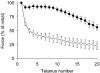
Skeletal muscle that is deficient in creatine kinase (CK-/-) exhibits accelerated glycogenolysis during contraction. Understanding this phenomenon could provide insight into the control of glycogenolysis during contraction. Therefore, glycogen breakdown was investigated in isolated extensor digitorum longus CK-/- muscle. Muscles were stimulated to produce repeated tetani for 20 s in the presence of sodium cyanide to block mitochondrial respiration. Accumulation of lactate after stimulation was similar in wild-type (WT) and CK-/- muscles, whereas accumulation of glucose-6-phosphate was twofold higher in CK-/- muscles, indicating greater glycogenolysis in CK-/- muscles. Total phosphorylase activity was decreased by almost 30 % in CK-/- muscle (P < 0.001). Phosphorylase fractional activity (-/+ 3.3 mM AMP) was similar in both groups in the basal state (about 10 %), but increased to a smaller extent in CK-/- muscles after stimulation (39 +/- 4 % vs. 52 +/- 4 % in WT, P < 0.05). Inorganic phosphate, the substrate for phosphorylase, increased marginally in CK-/- muscles after stimulation (basal = 25.3 +/- 2.2 micromol (g dry muscle)-1; stimulated = 33.9 +/- 2.3 micromol (g dry muscle)-1), but substantially in WT muscles (basal = 11.4 +/- 0.7 micromol (g dry muscle)-1; stimulated = 54.2 +/- 4.5 micromol (g dry muscle)-1). Kinetic studies of phosphorylase b (dephosphorylated enzyme) from muscle extracts in vitro demonstrated higher relative activities in CK-/- muscles (60-135 %) in response to low AMP concentrations (up to 50 microM) in both the basal state and after stimulation (P < 0.05), whereas no differences in activity between CK-/- and WT muscles were observed at high AMP concentrations (> 100 microM). These data indicate that allosteric activation of phosphorylase b accounts for the accelerated glycogenolysis in CK-/- muscle during contraction.
Figures
References
-
- Aragon JJ, Tornheim K, Lowenstein JM. On a possible role of IMP in the regulation of phosphorylase activity in skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1980;117:K56–64. - PubMed
-
- Broberg S, Katz A, Sahlin K. Propranolol enhances adenine nucleotide degradation in human muscle during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1988;65:2478–2483. - PubMed
-
- Brostrom CO, Hunkeler FL, Krebs EG. The relation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+ J Biol Chem. 1971;246:1961–1967. - PubMed
-
- Brown DH, Cori CF. Animal and plant polysaccharide phosphorylase. In: Boyer LM, editor. The Enzymes. Vol. 5. New York: Academic; 1961. pp. 207–228.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

