GABAB receptor- and metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent cooperative long-term potentiation of rat hippocampal GABAA synaptic transmission
- PMID: 12963794
- PMCID: PMC2343476
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.049015
GABAB receptor- and metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent cooperative long-term potentiation of rat hippocampal GABAA synaptic transmission
Abstract
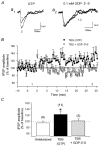
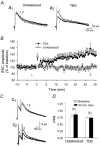
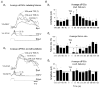
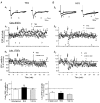
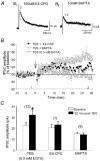
Repetitive stimulation of Schaffer collaterals induces activity-dependent changes in the strength of polysynaptic inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons that are dependent on stimulation parameters. In the present study, we investigated the effects of two stimulation patterns, theta-burst stimulation (TBS) and 100 Hz tetani, on pharmacologically isolated monosynaptic GABAergic responses in adult CA1 pyramidal cells. Tetanization with 100 Hz trains transiently depressed both early and late IPSPs, whereas TBS induced long-term potentiation (LTP) of early IPSPs that lasted at least 30 min. Mechanisms mediating this TBS-induced potentiation were examined using whole-cell recordings. The paired-pulse ratio of monosynaptic inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) was not affected during LTP, suggesting that presynaptic changes in GABA release are not involved in the potentiation. Bath application of the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP55845 or the group I/II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist E4-CPG inhibited IPSC potentiation. Preventing postsynaptic G-protein activation or Ca2+ rise by postsynaptic injection of GDP-beta-S or BAPTA, respectively, abolished LTP, indicating a G-protein- and Ca2+-dependent induction in this LTP. Finally during paired-recordings, activation of individual interneurons by intracellular TBS elicited solely short-term increases in average unitary IPSCs in pyramidal cells. These results indicate that a stimulation paradigm mimicking the endogenous theta rhythm activates cooperative postsynaptic mechanisms dependent on GABABR, mGluR, G-proteins and intracellular Ca2+, which lead to a sustained potentiation of GABAA synaptic transmission in pyramidal cells. GABAergic synapses may therefore contribute to functional synaptic plasticity in adult hippocampus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell-type specific GABA synaptic transmission and activity-dependent plasticity in rat hippocampal stratum radiatum interneurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jul;22(1):179-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04207.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16029207
-
Low-frequency stimulation induces a new form of LTP, metabotropic glutamate (mGlu5) receptor- and PKA-dependent, in the CA1 area of the rat hippocampus.Hippocampus. 2006;16(4):345-60. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20146. Hippocampus. 2006. PMID: 16302229
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission in the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus.Brain Res. 2010 Apr 14;1325:28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.02.021. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20153735
-
Do GABAA and GABAB inhibitory postsynaptic responses originate from distinct interneurons in the hippocampus?Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1997 May;75(5):520-5. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9250387 Review.
-
Postnatal maturation of gamma-aminobutyric acidA and B-mediated inhibition in the CA3 hippocampal region of the rat.J Neurobiol. 1995 Mar;26(3):339-49. doi: 10.1002/neu.480260306. J Neurobiol. 1995. PMID: 7775967 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterosynaptic long-term potentiation at GABAergic synapses of spinal lamina I neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 30;31(48):17383-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3076-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22131400 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial of SGS-742, a γ-aminobutyric acid B (GABA-B) Receptor Antagonist, for Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency.J Child Neurol. 2021 Nov;36(13-14):1189-1199. doi: 10.1177/08830738211012804. Epub 2021 May 20. J Child Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34015244 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
GABAergic gene expression in postmortem hippocampus from alcoholics and cocaine addicts; corresponding findings in alcohol-naïve P and NP rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029369. Epub 2012 Jan 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22253714 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory control of hippocampal inhibitory neurons.Front Neurosci. 2012 Nov 14;6:165. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00165. eCollection 2012. Front Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23162426 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi cell-mediated activation of postsynaptic GABA(B) receptors induces disinhibition of the Golgi cell-granule cell synapse in rat cerebellum.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043417. Epub 2012 Aug 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22937048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bashir ZI, Bortolotto ZA, Davies CH, Berretta N, Irving AJ, Seal AJ, Henley JM, Jane DE, Watkins JC, Collingridge GL. Induction of LTP in the hippocampus needs synaptic activation of glutamate metabotropic receptors. Nature. 1993;363:347–350. - PubMed
-
- Baude A, Nusser Z, Roberts JD, Mulvihill E, McIlhinney RA, Somogyi P. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1 alpha) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron. 1993;11:771–787. - PubMed
-
- Cartmell J, Schoepp DD. Regulation of neurotransmitter release by metabotropic glutamate receptors. J Neurochem. 2000;75:889–907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

