Both dorsal horn and lamina VIII interneurones contribute to crossed reflexes from feline group II muscle afferents
- PMID: 12963796
- PMCID: PMC2343445
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.048009
Both dorsal horn and lamina VIII interneurones contribute to crossed reflexes from feline group II muscle afferents
Abstract
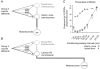
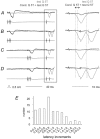
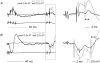
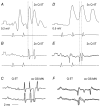
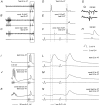
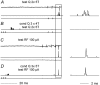
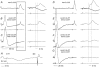
Previous studies have demonstrated that group II muscle afferents exert powerful actions on contralateral motoneurones and that these actions are mediated primarily via lamina VIII commissural interneurones. We examined whether dorsal horn interneurones also contribute to these actions, as they have been shown to contribute to the actions of group II afferents on ipsilateral motoneurones. We tested the susceptibility of IPSPs and EPSPs evoked from group II afferents in contralateral motoneurones to presynaptic inhibition as an indicator of the relative contribution of dorsal horn interneurones to these PSPs, since the monosynaptic activation of dorsal horn interneurones is more weakly and more briefly depressed by presynaptic inhibition than is the monosynaptic activation of lamina VIII and other intermediate zone and ventral horn interneurones. While the earliest components of IPSPs and EPSPs evoked by group II afferents were abolished by conditioning stimulation of group II afferents, consistent with them being evoked disynaptically by commissural interneurones, trisynaptic components of these PSPs were only partly reduced and are therefore attributed to dorsal horn interneurones. The same conditioning stimuli depressed the disynaptic excitation of lamina VIII commissural interneurones by group II afferents much less effectively than they depressed monosynaptic excitation, indicating that dorsal horn interneurones contribute to this disynaptic excitation. On the basis of these observations we conclude that that dorsal horn interneurones contribute to the late actions of group II muscle afferents on contralateral motoneurones through their disynaptic actions on commissural interneurones.
Figures

References
-
- Aggelopoulos NC, Edgley SA. Segmental localisation of the relays mediating crossed inhibition of hindlimb motoneurones from group II afferents in the anaesthetized cat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1995;185:60–64. - PubMed
-
- Alstermark B, Kummel H. Transneuronal transport of wheat germ agglutinin conjugated horseradish peroxidase into last order spinal interneurones projecting to acromio- and spinodeltoideus motoneurones in the cat. 1. Location of labelled interneurones and influence of synaptic activity on the transneuronal transport. Exp Brain Res. 1990;80:83–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

