Distinct geographic patterns of genetic diversity are maintained in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum) despite migration
- PMID: 12963820
- PMCID: PMC196885
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1633708100
Distinct geographic patterns of genetic diversity are maintained in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum) despite migration
Abstract
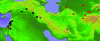
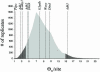
Mutations arise in a single individual and at a single point in time and space. The geographic distribution of mutations reflects both historical population size and frequency of migration. We employ coalescence-based methods to coestimate effective population size, frequency of migration, and level of recombination compatible with observed genealogical relationships in sequence data from nine nuclear genes in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum), a highly self-fertilizing grass species. In self-fertilizing plants, gamete dispersal is severely limited; dissemination occurs primarily through seed dispersal. Also, heterozygosity is greatly reduced, which renders recombination less effective at randomizing genetic variation and causes larger portions of the genome to trace a similar history. Despite these predicted effects of this mating system, the majority of loci show evidence of recombination. Levels of nucleotide variation and the patterns of geographic distribution of mutations in wild barley are highly heterogeneous across loci. Two of the nine sampled loci maintain highly diverged, geographic region-specific suites of mutations. Two additional loci include region-specific haplotypes with a much shallower coalescence. Despite inbreeding, sessile growth habit, and the observation of geographic structure at almost half of sampled loci, parametric estimates of migration suggest that seed dispersal is sufficient for migration across the approximately 3,500-km range of the species. Recurrent migration is also evident based on the geographic distribution of mutational variation at some loci. At one locus a single haplotype has spread rapidly enough to occur, unmodified by mutation, across the range of the species.
Figures

References
-
- Barton, N. H. & Wilson, I. (1995) Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B 349, 49–59. - PubMed
-
- Kingman, J. F. C. (1982) Stochastic Processes: Formalism Appl. Prc. Winter Sch. 13, 235–248.
-
- Hudson, R. R. (1990) in Oxford Survey of Evolutionary Biology, eds. Dawkins, R. & Ridley, M. (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford), Vol. 7, pp. 1–44.
-
- Notohara, M. (1990) J. Math. Biol. 29, 59–75. - PubMed
-
- Takahata, N. (1988) Genet. Res. 52, 213–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

