Neutralization of measles virus infectivity and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activity against an Epstein-Barr virus-infected cell line by intravenous immunoglobulin G [corrected]
- PMID: 12965899
- PMCID: PMC193912
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.10.5.751-756.2003
Neutralization of measles virus infectivity and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activity against an Epstein-Barr virus-infected cell line by intravenous immunoglobulin G [corrected]
Erratum in
- Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003 Nov;10(6):1161
Abstract
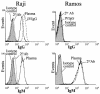
Patients with antibody deficiency disorders are highly susceptible to microbial infections. Intravenous (i.v.) immunoglobulin concentrates were originally developed as replacement therapy for such patients. The present study assesses the measles virus neutralizing antibody titers and the antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) capacities against Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected cells of immunoglobulin G (IgG) preparations produced for i.v. use (i.v. IgG). The level of neutralizing antibodies against measles virus was determined by a syncytium neutralization test with Vero cells as targets. The measles virus neutralizing antibody titers of the i.v. IgG preparations were >3 x 10(2) and were an average of 1.0 log higher than the titers in pooled plasma from healthy subjects. The two IgG preparations tested showed similar ADCC activities against EBV-infected Raji cells, being active at concentrations of 3 mg/ml or higher. i.v. IgG bound to Raji cells but not to the EBV-negative Ramos cells, as evaluated by flow cytometry. Our in vitro findings may provide further support for the use of i.v. IgG for the prevention and treatment of infections caused by specific viral pathogens.
Figures


References
-
- Bartz, R., R. Firsching, B. Rima, V. ter Meulen, and J. Schneider-Schaulies. 1998. Differential receptor usage by measles virus strains. J. Gen. Virol. 79:1015-1025. - PubMed
-
- Beckford, A. P., R. O. Kaschula, and C. Stephen. 1985. Factors associated with fatal cases of measles. A retrospective autopsy study. S. Afr. Med. J. 68:858-863. - PubMed
-
- Biron, C. A., K. S. Byron, and J. L. Sullivan. 1989. Severe herpesvirus infections in an adolescent without natural killer cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 320:1731-1735. - PubMed
-
- Borges, M. B., G. F. Mann, and S. Freire Mda. 1996. Biological characterization of clones derived from the Edmonston strain of measles virus in comparison with Schwarz and CAM-70 vaccine strains. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 91:507-513. - PubMed
-
- Bottino, C., M. Falco, S. Parolini, E. Marcenaro, R. Augugliaro, S. Sivori, E. Landi, R. Biassoni, L. D. Notarangelo, L. Moretta, and A. Moretta. 2001. NTB-A [correction of GNTB-A], a novel SH2D1A-associated surface molecule contributing to the inability of natural killer cells to kill Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. J. Exp. Med. 194:235-246. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

