Molecular inflammatory responses measured in blood of patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia
- PMID: 12965910
- PMCID: PMC193876
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.10.5.813-820.2003
Molecular inflammatory responses measured in blood of patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia
Abstract
In order to analyze the characteristics of the inflammatory response occurring in blood during pneumonia, we studied 38 patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia. Venous and arterial blood samples were collected at study entry and on days 1, 2, 3, 5, and 7 after inclusion. The concentrations of proinflammatory (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-alpha], interleukin 1beta [IL-1beta], IL-6, and IL-8) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines were determined in order to detect differences related to the origin of the sample, the causative organism, the clinical variables, and the final outcome of the episode. Legionella pneumonia infections showed higher concentrations of TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10. After 24 h, plasma IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 concentrations in pneumococcal episodes increased, whereas in the same time interval, cytokine concentrations in Legionella episodes markedly decreased. The characteristics of the inflammatory response in bacteremic pneumococcal episodes were different from those in nonbacteremic episodes, as indicated by the higher plasma cytokine concentrations in the former group. Finally, our analysis of cytokine concentrations with regard to the outcome--in terms of the need for intensive care unit admittance and/or mechanical ventilation as well as mortality--suggests that there is a direct relationship between the intensity of the inflammatory response measured in blood and the severity of the episode.
Figures

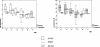

References
-
- American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 1999. International Consensus Conferences in Intensive Care Medicine: ventilator-associated lung injury in ARDS. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 160:2118-2124. - PubMed
-
- Austrian, R., and J. Gold. 1964. Pneumococcal bacteriemia with special reference to bacteriemic pneumococcal pneumonia. Ann. Intern. Med. 6:759-770. - PubMed
-
- Bethmann, A. N., F. Brasch, R. Nüsing, K. Vogt, H. D. Volk, K. M. Müller, A. Wendel, and S. Uhlig. 1998. Hyperventilation induces release of cytokines from perfused mouse lung. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 157:263-272. - PubMed
-
- Busund, R., R. O. Lindsetmo, and I. T. Rasmussen. 1990. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 appearance in experimental Gram-negative septic shock. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 116:100-105. - PubMed
-
- Creasey, A. A., P. Stevens, and J. Kenney. 1991. Endotoxin and cytokine profile in plasma baboons challenged with lethal and sublethal Escherichia coli. Circ. Shock 33:84-91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

