TNF-alpha increases human melanoma cell invasion and migration in vitro: the role of proteolytic enzymes
- PMID: 12966436
- PMCID: PMC2376936
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601257
TNF-alpha increases human melanoma cell invasion and migration in vitro: the role of proteolytic enzymes
Abstract
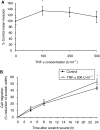
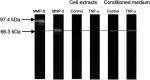
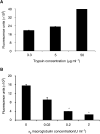
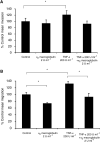
Inflammatory mediators have been reported to promote malignant cell growth, invasion and metastatic potential. More specifically, we have recently reported that tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) increases melanoma cell attachment to extracellular matrix (ECM) substrates and invasion through fibronectin. In this study, we extend these investigations asking specifically whether the TNF-alpha effect on cell invasion and migration involves activation of proteolytic enzymes. We examined the effect of TNF-alpha on melanoma expression/activation of type IV gelatinases matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 (MMPs -2 and -9) and general proteolytic enzymes. Stimulation with TNF-alpha significantly increased both melanoma cell migration at 24 h (+21%) and invasion through fibronectin (+35%) but did not upregulate/activate the expression of latent MMP-2 constitutively produced by these cells and did not upregulate their general protease activity. However, the increased cell migration and invasion through fibronectin observed following stimulation with TNF-alpha were inhibited by the general protease inhibitor alpha(2) macroglobulin. These findings suggest that the promigratory and proinvasive effect of TNF-alpha on this melanoma cell line may be mediated to some extent by induction of localised cell membrane-bound degradative enzyme activity, which is not readily detected in biochemical assays.
Figures
References
-
- Ahonen M, Poukkula M, Baker AH, Kashiwagi M, Nagase H, Eriksson JE, Kähäri V-M (2003) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 induces apoptosis in melanoma cells by stabilization of death receptors. Oncogene 22: 2121–2134 - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F (2002) Tumor necrosis factor or tumor promoting factor? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13: 135–141 - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2001) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357: 539–545 - PubMed
-
- Baugh MD, Perry MJ, Hollander AP, Davies RD, Cross SS, Lobo AJ, Taylor CJ, Evans GS (1999) Matrix metalloproteinase levels are elevated in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 117: 814–822 - PubMed
-
- Beutler BA (1999) The role of tumor necrosis factor in health and disease. J Rheumatol 26S(57): 16–21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

