An anti-MUC1-antibody-interleukin-2 fusion protein that activates resting NK cells to lysis of MUC1-positive tumour cells
- PMID: 12966437
- PMCID: PMC2376954
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601267
An anti-MUC1-antibody-interleukin-2 fusion protein that activates resting NK cells to lysis of MUC1-positive tumour cells
Abstract
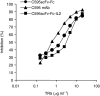
MUC1 mucin is aberrantly glycosylated and overexpressed in a number of epithelial malignancies and is therefore a promising tumour-associated antigen for target-directed immunotherapy of a panel of malignant diseases. In MUC1-positive tumours, MHC class I expression is frequently downregulated and MUC1-specific cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) are either not available or in a state of anergy allowing tumour growth without limitation by CTL control. To activate lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells, we here generated an anti-MUC1-scFv-IL2 fusion protein (C595scFv-Fc-IL2) that contains the C595 single-chain antibody for MUC1 binding, the human IgG1 CH2CH3 domain for protein dimerisation, and interleukin-2 (IL2) for activation of immunological effector cells. The fusion protein binds to MUC1-derived peptides and to MUC1-positive tumour cells with the same specificity as does the C595 monoclonal antibody. Bound to MUC1, the C595scFv-Fc-IL2 fusion protein stimulates proliferation of human activated lymphocytes in vitro. Upon binding to MUC1-positive MCF7 breast carcinoma cells, moreover, the fusion protein activates resting NK cells to tumour cell lysis. These properties make the C595scFv-Fc-IL2 fusion protein a suitable candidate for the immunotherapy of MUC1-positive tumours.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Activation of human effector cells by a tumor reactive recombinant anti-ganglioside GD2 interleukin-2 fusion protein (ch14.18-IL2).Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Dec;2(12):1951-9. Clin Cancer Res. 1996. PMID: 9816154
-
Immune recognition of tumor-associated mucin MUC1 is achieved by a fully synthetic aberrantly glycosylated MUC1 tripartite vaccine.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jan 3;109(1):261-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115166109. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22171012 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of MUC1 mucin as an escape mechanism of breast cancer cells from autologous cytotoxic T-lymphocytes.Br J Cancer. 2001 May 4;84(9):1258-64. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1744. Br J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11336479 Free PMC article.
-
Re-targeting of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and/or natural killer cells to CEA-expressing tumor cells with anti-CEA antibody activity.Anticancer Res. 2005 Nov-Dec;25(6A):3725-32. Anticancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16302732 Review.
-
Tecemotide: an antigen-specific cancer immunotherapy.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3383-93. doi: 10.4161/hv.29836. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25483673 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL12 integrated into the CAR exodomain converts CD8+ T cells to poly-functional NK-like cells with superior killing of antigen-loss tumors.Mol Ther. 2022 Feb 2;30(2):593-605. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.10.011. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34678512 Free PMC article.
-
NK Cell Hyporesponsiveness: More Is Not Always Better.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 12;20(18):4514. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184514. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31547251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of circulating anti-mucin 1 (MUC1) antibodies in breast tumor patients by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a recombinant MUC1 protein containing six tandem repeats and expressed in Escherichia coli.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010 Dec;17(12):1903-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00142-10. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20876819 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic efficacy of tumor-targeted IL2 in LTalpha(-/-) mice depends on conditioned T cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006 Jul;55(7):861-6. doi: 10.1007/s00262-005-0076-8. Epub 2005 Sep 13. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006. PMID: 16158274 Free PMC article.
-
Combining the Specific Anti-MUC1 Antibody TAB004 and Lip-MSA-IL-2 Limits Pancreatic Cancer Progression in Immune Competent Murine Models of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2019 Apr 30;9:330. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00330. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31114758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal B, Krantz MJ, Parker J, Longenecker BM (1998) Expression of Muc1 mucin on activated human T cells: implications for a role of muc1 in normal immune regulation. Cancer Res 58: 4079–4081 - PubMed
-
- Apostolopoulos V, Karanikas V, Haurum JS, McKenzie IF (1997) Induction of HLA-A2-restricted CTLs to the mucin 1 human breast cancer antigen. J Immunol 159: 5211–5218 - PubMed
-
- Berruti A, Tampellini M, Torta M, Buniva T, Gorzegno G, Dogliotti L (1994) Prognostic value in predicting overall survival of two mucinous markers: CA 15-3 and CA 125 in breast cancer patients at first relapse of disease. Eur J Cancer 30A: 2082–2084 - PubMed
-
- Brossart P, Heinrich KS, Stuhler G, Behnke L, Reichardt VL, Stevanovic S, Muhm A, Rammensee HG, Kanz L, Brugger W (1999) Identification of HLA-A2-restricted T-cell epitopes derived from the MUC1 tumor antigen for broadly applicable vaccine therapies. Blood 93: 4309–4317 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

