Severe tungiasis in underprivileged communities: case series from Brazil
- PMID: 12967492
- PMCID: PMC3020603
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0908.030041
Severe tungiasis in underprivileged communities: case series from Brazil
Abstract
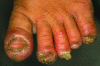
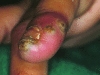
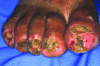
Tungiasis is caused by infestation with the sand flea (Tunga penetrans). This ectoparasitosis is endemic in economically depressed communities in South American and African countries. Tungiasis is usually considered an entomologic nuisance and does not receive much attention from healthcare professionals. During a study on tungiasis-related disease in an economically depressed area in Fortaleza, northeast Brazil, we identified 16 persons infested with an extremely high number of parasites. These patients had >50 lesions each and showed signs of intense acute and chronic inflammation. Superinfection of the lesions had led to pustule formation, suppuration, and ulceration. Debilitating sequelae, such as loss of nails and difficulty in walking, were constant. In economically depressed urban neighborhoods characterized by a high transmission potential, poor housing conditions, social neglect, and inadequate healthcare behavior, tungiasis may develop into severe disease.
Figures


References
-
- Ejezie GC. The parasitic diseases of school children in Lagos State, Nigeria. Acta Trop. 1981;38:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Heukelbach J, Feldmeier H. Tungiasis in poor communities of Northeast Brazil: an important public health problem. Public Health (Bayer). 2002;16:79–87.
-
- Matias RS. Epidemia de tungíase no Rio Grande do Sul. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 1989;22:137–42. - PubMed
-
- Hoeppli R. Early references to the occurrence of Tunga penetrans in Tropical Africa. Acta Trop. 1963;20:143–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
