Atypical beta-adrenoceptors, different from beta 3-adrenoceptors and probably from the low-affinity state of beta 1-adrenoceptors, relax the rat isolated mesenteric artery
- PMID: 12967929
- PMCID: PMC1574016
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705421
Atypical beta-adrenoceptors, different from beta 3-adrenoceptors and probably from the low-affinity state of beta 1-adrenoceptors, relax the rat isolated mesenteric artery
Abstract
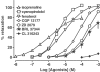
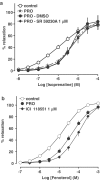
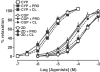
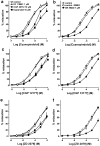
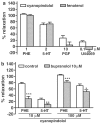
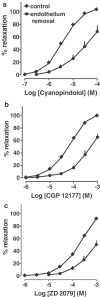
(1) We examined whether beta3- and/or atypical beta-adrenoceptors relax the rat isolated mesenteric artery. (2) Mesenteric arteries precontracted with phenylephrine were relaxed by beta-agonists with the following potencies (pD2): nonselective agonist isoprenaline (6.00)>nonconventional partial agonist cyanopindolol (5.45)>beta2-agonist fenoterol (4.98)>nonconventional partial agonist CGP 12177 (4.19)>beta3-agonist ZD 2079 (3.72). The beta3-agonist CL 316243 1 mm relaxed the vessel only marginally. (3) The concentration-response curves (CRCs) for cyanopindolol, CGP 12177 and ZD 2079 were not affected by the nonselective beta-antagonist propranolol 0.3 microm, the beta2-antagonist ICI 118551 1 microm and by CL 316243 60 microm, but shifted to the right by bupranolol (pA2 5.3-5.7), CGP 20712 (5.4) and SR 59230A (6.5-6.7) (the latter three drugs block atypical and/or beta3-adrenoceptors at high concentrations). (4) The CRC for isoprenaline was shifted to the right by propranolol (pA2 7.0) but, in the presence of propranolol 0.3 microm, not affected by SR 59230A 1 microm. The CRC for fenoterol was shifted to the right by propranolol (pA2 6.9) and ICI 118551 (6.8). (5) Removal of endothelium diminished the vasorelaxant effects of cyanopindolol, CGP 12177 and ZD 2079. (6) Fenoterol and cyanopindolol also relaxed (endothelium-intact) mesenteric arteries precontracted with serotonin. The relaxant effect of cyanopindolol was antagonized by bupranolol to about the same degree as in phenylephrine-contracted vessels. (7) In conclusion, beta2- and atypical beta-adrenoceptors (but not beta3-adrenoceptors) relax the rat mesenteric artery. The atypical beta-adrenoceptor, which is partially located endothelially, may differ from the low-affinity state of the beta1-adrenoceptor.
Figures
Comment in
-
The 'state' of beta-adrenoceptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Sep;140(1):1-2. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705420. Epub 2003 Aug 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12967928 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- BLOOM J.D., DUTIA M.D., JOHSON B.D., WISSNER A., BURNS M.G., BURNS LARGIS E.E., DOLAN J.A., CLAUS T.H. Disodium (R,R)-5-[2-[(3-chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]-amino-propyl]-l,3-benzodioxole-2,2-dicarboxylate (CL 316,243): a potent β-adrenergic agonist virtually specific for β3 receptors. A promising antidiabetic and antiobesity agent. J. Med. Chem. 1992;35:3081–3084. - PubMed
-
- BRAWLEY L., SHAW A.M., MACDONALD A. Role of endothelium/nitric oxide in atypical beta-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation in rat isolated aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000b;398:285–296. - PubMed
-
- BRODDE O.-E., MICHEL M.C. Adrenergic and muscarinic receptors in the human heart. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999;51:651–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

