Capacitative calcium entry as a pulmonary specific vasoconstrictor mechanism in small muscular arteries of the rat
- PMID: 12967939
- PMCID: PMC1574006
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705408
Capacitative calcium entry as a pulmonary specific vasoconstrictor mechanism in small muscular arteries of the rat
Abstract
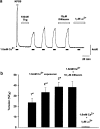
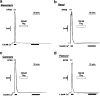
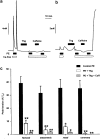
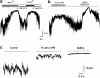
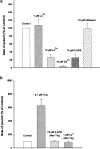
(1) The effect of induction of capacitative Ca2+ entry (CCE) upon tone in small (i.d. 200-500 microm) intrapulmonary (IPA), mesenteric (MA), renal (RA), femoral (FA), and coronary arteries (CA) of the rat was examined. (2) Following incubation of IPA with 100 nm thapsigargin (Thg) in Ca2+-free physiological salt solution (PSS), a sustained contraction was observed upon reintroduction of 1.8 mm Ca2+, which was unaffected by either diltiazem (10 microm) or the reverse mode Na+/Ca2+ antiport inhibitor KB-R7943 (10 microm). An identical protocol failed to elicit contraction in MA, RA, or CA, while a small transient contraction was sometimes observed in FA. (3) The effect of this protocol on the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) was assessed using Fura PE3-loaded IPA, MA, and FA. Reintroduction of Ca2+ into the bath solution following Thg treatment in Ca2+-free PSS caused a large, rapid, and sustained increase in [Ca2+]i in all the three types of artery. (4) 100 nm Thg induced a slowly developing noisy inward current in smooth muscle cells (SMC) isolated from IPA, which was due to an increase in the activity of single channels with a conductance of approximately 30 pS. The current had a reversal potential near 0 mV in normal PSS, and persisted when Ca2+-dependent K+ and Cl- currents were blocked; it was greatly inhibited by 1 microm La3+, 1 microm Gd3+, and the IP3 receptor antagonist 2-APB (75 microm), and by replacement of extracellular cations by NMDG+. (5) In conclusion, depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores with Thg caused capacitative Ca2+ entry in rat small muscular IPA, MA, and FA. However, a corresponding contraction was observed only in IPA. CCE in IPA was associated with the development of a small La3+- and Gd3+-sensitive current, and an increased Mn2+ quench of Fura PE-3 fluorescence. These results suggest that although CCE occurs in a number of types of small arteries, its coupling to contraction appears to be of particular importance in pulmonary arteries.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Actions of 4-chloro-3-ethyl phenol on internal Ca2+ stores in vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Oct;122(3):504-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701389. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9351507 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine-induced vasoconstriction of pulmonary artery: activation of non-store-operated Ca2+ entry.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Oct 1;68(1):56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.05.013. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15950201
-
Mechanisms of the prostaglandin F2alpha-induced rise in [Ca2+]i in rat intrapulmonary arteries.J Physiol. 2006 Feb 15;571(Pt 1):147-63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.101394. Epub 2005 Dec 15. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16357015 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-independent calcium entry in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction of intrapulmonary arteries of the rat.J Physiol. 2000 Jun 15;525 Pt 3(Pt 3):669-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00669.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10856120 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of capacitative and non-capacitative Ca2+ entry in A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells.Biol Res. 2004;37(4):641-5. doi: 10.4067/s0716-97602004000400020. Biol Res. 2004. PMID: 15709692 Review.
Cited by
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 decreases TRPC expression, store-operated Ca(2+) entry, and basal [Ca(2+)]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 May 1;304(9):C833-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00036.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23447035 Free PMC article.
-
Superoxide differentially controls pulmonary and systemic vascular tone through multiple signalling pathways.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Jan 1;89(1):214-24. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq275. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 20805095 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction.Physiol Rev. 2012 Jan;92(1):367-520. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00041.2010. Physiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22298659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute hypoxia activates store-operated Ca(2+) entry and increases intracellular Ca(2+) concentration in rat distal pulmonary venous smooth muscle cells.J Thorac Dis. 2013 Oct;5(5):605-12. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.08.68. J Thorac Dis. 2013. PMID: 24255773 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of acid-sensing ion channel 2 enhances pulmonary vascular resistance and hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Aug 1;127(2):393-407. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00894.2018. Epub 2019 Jun 6. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 31169471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ARNON A., HAMLYN J.M., BLAUSTEIN M.P. Na+ entry via store-operated channels modulates Ca2+ signalling in arterial myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 2000;278:C163–C173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

