The similarities and diversities of signal pathways leading to consolidation of conditioning and consolidation of extinction of fear memory
- PMID: 12967993
- PMCID: PMC6740702
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-23-08310.2003
The similarities and diversities of signal pathways leading to consolidation of conditioning and consolidation of extinction of fear memory
Abstract
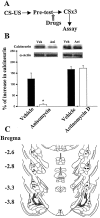
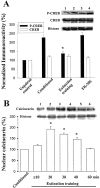
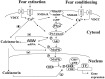
It is generally believed that consolidation of long-term memory requires activation of protein kinases, transcription of genes, and new protein synthesis. However, little is known about the signal cascades involved in the extinction of memory, which occurs when the conditioned stimulus is no longer followed by the unconditioned stimulus. Here, we show for the first time that an intra-amygdala injection of transcription inhibitor actinomycin D at the dose that blocked acquisition failed to affect extinction of a learned response. Conversely, protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin blocked both acquisition and extinction. Extinction training-induced expression of calcineurin was blocked by anisomycin but not by actinomycin D. NMDA receptor antagonist, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI-3 kinase), and MAP kinase inhibitors that blocked the acquisition also blocked the extinction of conditioned fear. Likewise, PI-3 kinase inhibitor blocked fear training-induced cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) phosphorylation as well as extinction training-induced decrease in CREB phosphorylation, the latter of which was associated with calcineurin expression and could be reversed by a specific calcineurin inhibitor. Thus, molecular processes that underlie long-term behavioral changes after acquisition and extinction share some common mechanisms and also display different characteristics.
Figures



References
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD ( 1998) The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci 7 : 602-609. - PubMed
-
- Bailey DJ, Kim JJ, Sun W, Thompson RF, Helmstetter FJ ( 1999) Acquisition of fear conditioning in rats requires the synthesis of mRNA in the amygdala. Behav Neurosci 113 : 276-282. - PubMed
-
- Barco A, Alarcon JM, Kandel ER ( 2002) Expression of constitutively active CREB protein facilitates the late phase of long-term potentiation by enhancing synaptic capture. Cell 108 : 689-703. - PubMed
-
- Baum M ( 1988) Spontaneous recovery from the effects of flooding (exposure) in animals. Behav Res Ther 26 : 185-186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
